PhD Candidate/Geography June 2025 (Anticipated)
Department of Geography
University at Buffalo Buffalo, NY
M.S. Epidemiology May 2020
School of Public Health
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics
University of Albany Albany, NY
B.S. Biological Sciences May 2018
Department of Biological Sciences
University at Albany Albany, NY
Research Focus
O’Connor’s doctoral research focuses on the spatial ecology and epidemiology of tick borne diseases in New York State. In particular, his dissertation work examines two genetic variants of Anaplasma phagocytophilum, the pathogen that causes anaplasmosis. Anaplasmosis is the second most frequent tick borne disease in New York State behind Lyme disease. An August 2021 article in Medscape reported Anaplasma cases nearly quadrupled statewide from 2010 to 2018. On a larger scale, Anaplasmosis became a nationally notifiable disease in the United States during 1999 after nationwide case counts increased significantly. Most of these infections occur in the upper midwestern and northeastern states, with eastern New York and the Hudson River Valley areas being of particular focus and concentration.
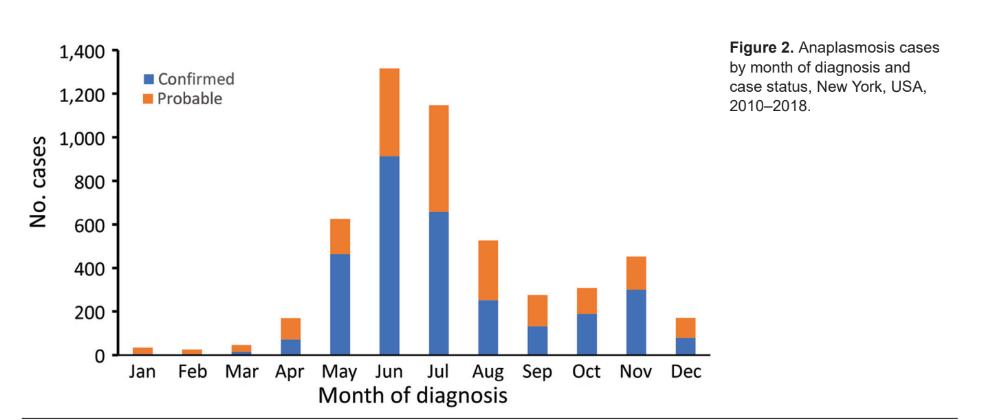
It comes as no surprise that confirmed Anaplasmosis are the highest during the summer months when people are active in the outdoors.
Background
O’Connor started his research on anaplasmosis while working on his masters degree at UAlbany with a team of other public health researchers and scientists in both academia and government. Their ongoing and collective research focuses on evaluating human risk of acquiring anaplasmosis (as well as Lyme Disease, babesiosis and other tickborne diseases) at publically accessible lands, based on measures of tick density and pathogen prevalence. Central to the investigation is looking at the relationships between human activity and environmental characteristics of specific land cover types supporting mammalian populations which serve as both transmitters and hosts of the A. phagocytophilum pathogen.
O’Connor’s research involves numerous datasets as part of his research, most notably human case data – which is analyzed at the ZIP Code Tabulation Area (ZCTA) level – as reported to the New York State Department of Health (NYSDOH). Data is aggregated by NYS regions (Capital, Central, Metro, and Western) and ZCTA by using patient address and 2010 US Census population data and shapefiles.
