Program’s modest beginning started in the late 1990s with AutoCAD files and a copy of ArcInfo
Now spending a significant amount of time upstate New York in Essex County, we now find ourselves looking for different routes to take back and forth from southeast New York State instead of the “go-to” I87/Northway option every time. Just to mix things up – the four-plus hour drive going the normal route can get to be a bit monotonous.
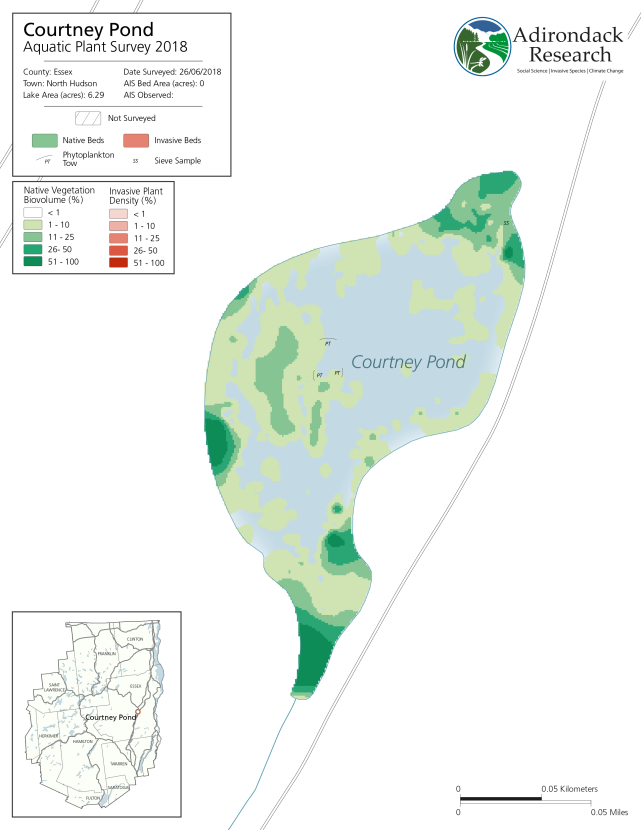
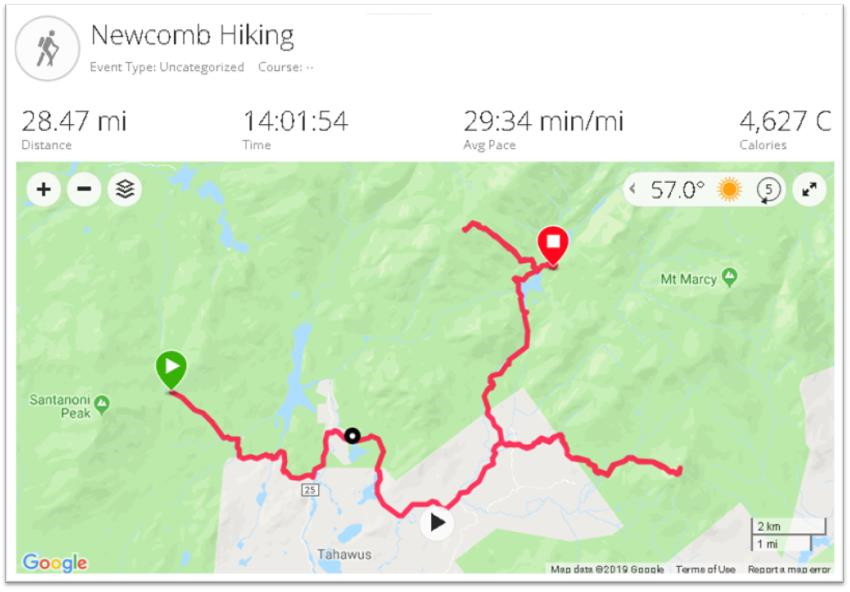
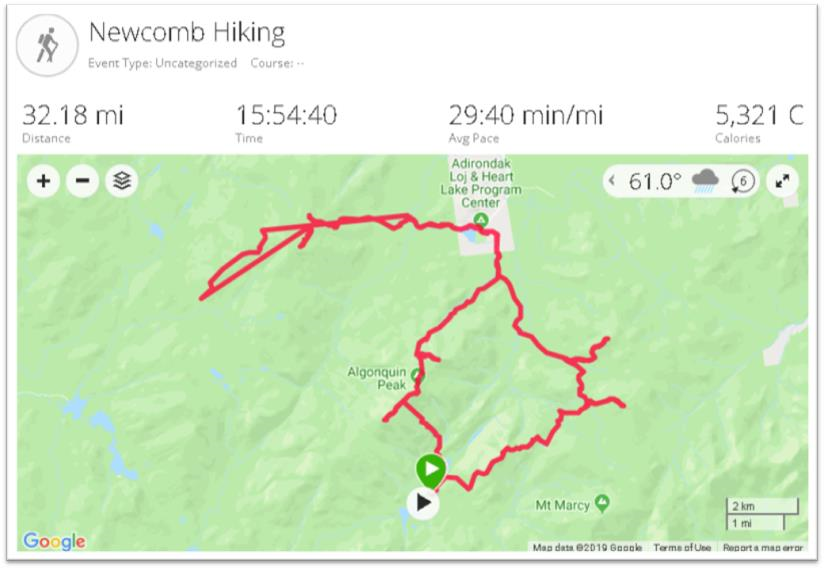
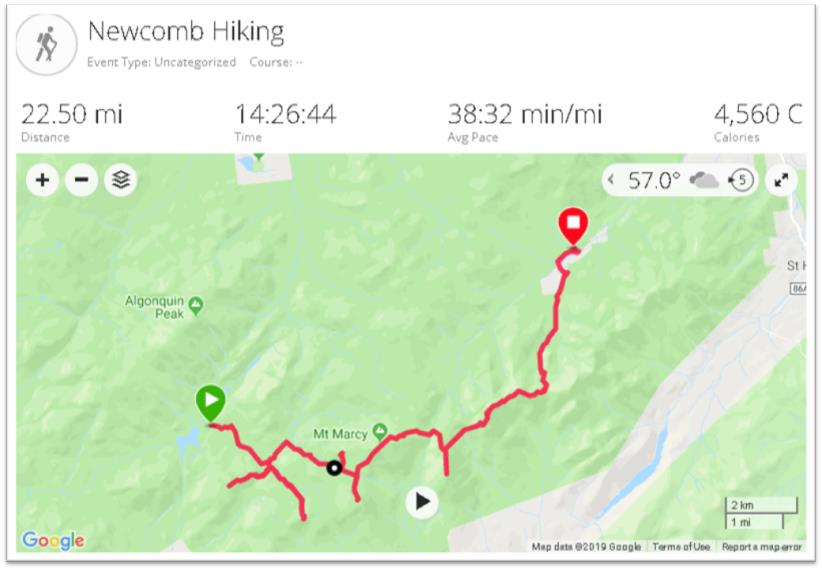
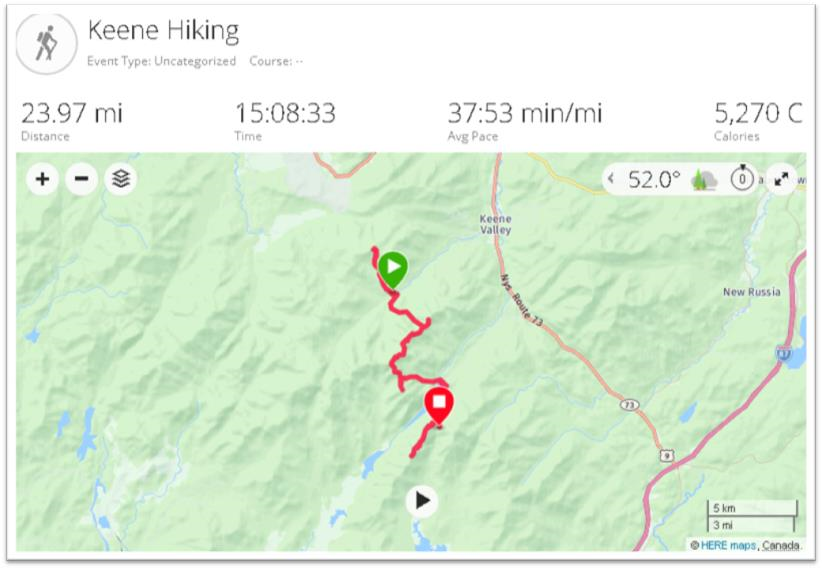
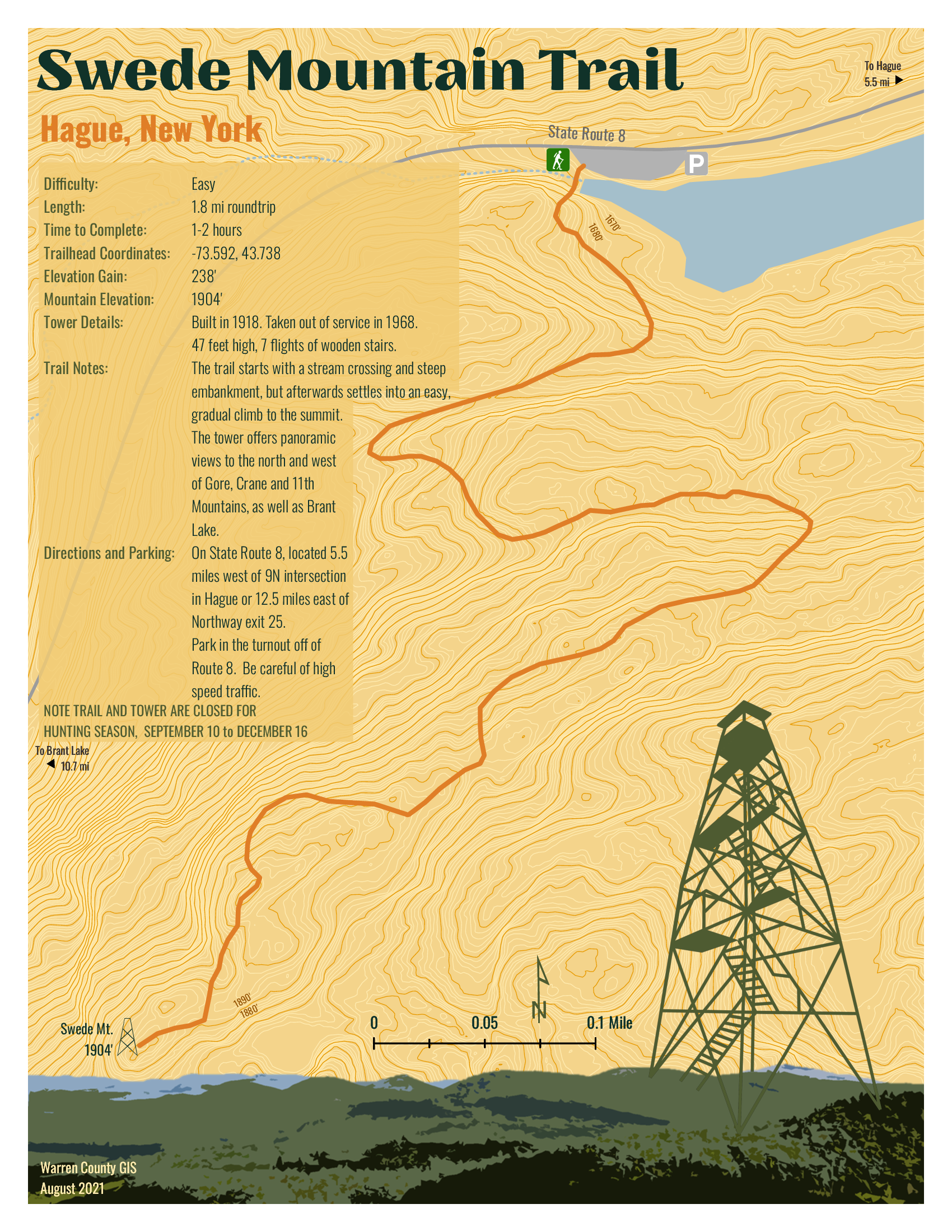
So it was in September I came south out of Ticonderoga headed to Hague (yes, named after The Hague in the Netherlands) on the northern end of Lake George – an area I had never been to. And it did not disappoint. Though ultimately to State Route 8 (aka Graphite Mountain Road) to a new Adirondacks trailhead: Swede Mountain Firetower. Even though the round-trip hike isn’t that long and relatively easy, it was getting late and I didn’t even get out of the car while in the trailhead parking lot. Instead, making a note to print out a trail map when I got home. A couple days later and not having a clue what trail maps were actually available, I Googled “Swede Mountain Firetower trail map” and a candidate list of URLs and image options were immediately returned. Randomly selecting the one below, the cartography caught my eye and I quickly looked for the map’s author. There on the bottom left: Warren County GIS.
It was quickly then off to the Warren County GIS website. Which became the genesis of this article.
Warren County GIS
Just by coincidence, this article coincides with the release of the new Warren County GIS Hub as announced by long-time county GIS Administrator, Sara Frankenfeld. Overseeing a countywide GIS program judiciously developed over the course of more than two decades – from the days of ARC/INFO coverages to 2022 mobile field apps and interactive online viewing applications. Also available through the program and Hub is a rich repository of dozens of hardcopy maps available for download covering areas such as countywide outdoor recreation, history, demographics, municipalities, planning and the environment and much more. An amazing amount of content bundled into three main categories: Web Maps and Apps | Maps for Print | Download Data.
Background
Originally from the northside of San Francisco Bay in Marin County and earning a degree in Geography from Northern Arizona University, Frankenfeld came to the east coast to initially start work with Dutchess County. After a short stint with NYSDEC she ultimately made her way to Warren County in 1999 where she got started with a copy of ARC/INFO on a standalone computer in the county building basement. The county had created a new GIS position in the Planning Department to help convert the tax maps to AutoCAD and then over a period of time converting from AutoCAD to ARC/INFO and then later to geodatabase.
Over the next four years, she was successful in winning over several other departments on the value and usefulness of GIS technology which she accomplished by focusing on easy, visible “wins” such getting people to use the newly available digital tax parcel data (linked to the RPS data) as quickly as possible and making hardcopy maps. Lots of maps. The visibility of the Warren County program also expanded by her working with municipal government zoning administrators and assessors and providing access to the new digital parcel data and including zoning maps, wetlands data, and FEMA floodplain maps. A New York State Archives and Administration (SARA) grant enabled the development of a parcel viewer app sby AppliedGIS – where she would later go to work for several years – called the Spatial Data Viewer. The groundwork was also laid for the implementation of ArcIMS and Imagemate Online. Somehow she also found time to include outreach programs to local schools and GIS Day.
After a period in the private sector with (then) AppliedGIS/Fountains Spatial, she returned to Warren County in 2013 where she remains today.
Today’s Environment
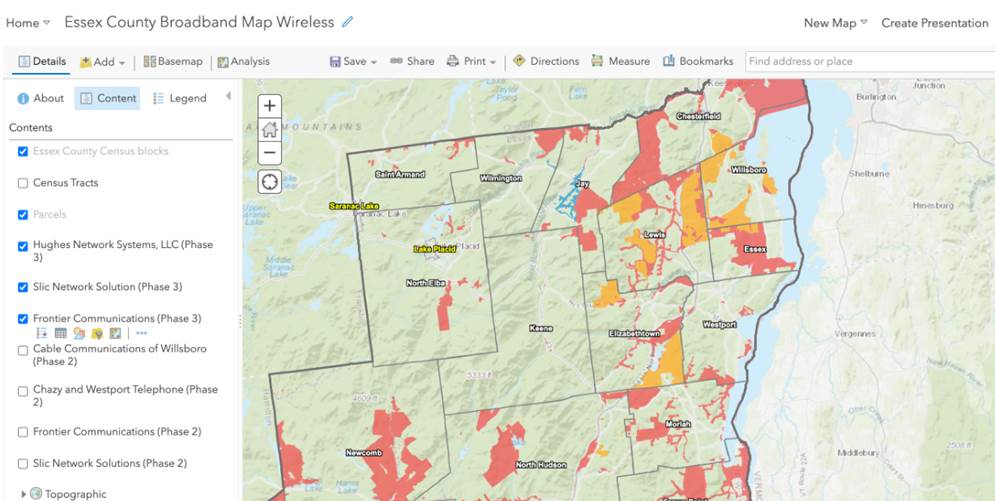
In 2022, the Warren County GIS program is built totally around the ArcGIS Online (AGOL) environment. Frankenfeld states AGOL has “totally transformed the workplace” and furthers her two main goals of (1) improving public access to data and (2) streamlining/improving processes for county departments and organizations the GIS program supports. She, along with GIS Specialist Amanda Beck, have embraced StoryMaps, Dashboards, Hubs and Survey123 in ways to make it easy for non-tech users to create and maintain data and access it. While many of the combo Survey123/dashboard applications are internal facing, others, like the Lake George Milfoil Harvesting real-time app is available to the public. And so is the Capital Improvement Project Planning viewer. Both respond to GIS requests from local municipalities, local organizations including the Adirondack/Glens Falls Transportation Council (AGFTC), Lake George Park Commission and the Lake Champlain Lake George Regional Planning Board – all of which have tech support contracts the County. Projects range from data compilation to hardcopy map preparation to creating and supporting online apps. Usually these three organizations know exactly what they want, but GIS staff we do often try to suggest ways to streamline or improve their requests. For example, County GIS staff helped AGFTC come up with a method to inventory sidewalk/crosswalk/curb ramps for ADA transition plans that proved really popular and resulted in a training session for all the Metropolitan Planning Organizations (MPO) in the state.
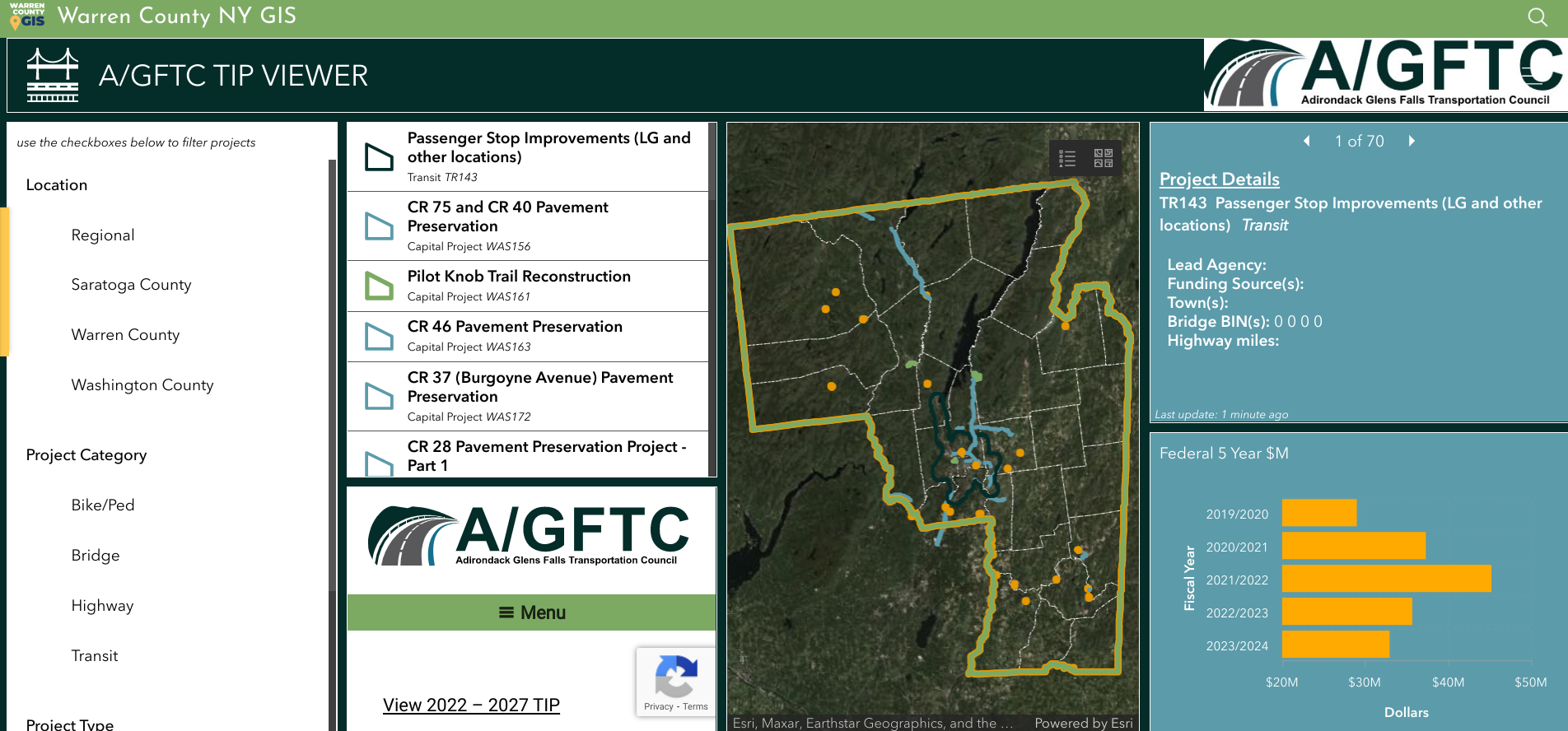
Dashboard for Adirondack/Glens Falls Transportation Council’s Transportation Improvement Program projects.
Having transitioned to ArcGIS Pro to support data editing, cartography and more complex analysis, Warren County GIS staff do a majority of their work in AGOL which includes the mobile pieces Field Maps and Survey123. They still collect GPS data as needed (usually related to recreation or e911) and support field operations, such as collecting milfoil harvest or infrastructure data, for other users. They also have Trimble boosters and cell phones which can be checked out to both county staff and municipalities for field data collection along with field worker licenses. While there are still a few remaining ArcGIS desktop users, most users are using AGOL with named users in Planning, Soil and Water, Public Affairs, the Sheriff’s Department, Office of Emergency Services, Public Works, and Parks and Recreation. Address and road centerlines are uploaded to the state twice a year and parcel data once a year. A large current project Sara and Amanda are currently working on is building additional GIS capacity and functionality in County Department of Public Works.
Except for Queensbury which has its own full-time GIS staff person, Warren County GIS supports all municipalities in the County. At the beginning of the program, Sara had set up each municipality with desktop GIS as well as providing training and support. In hindsight and it comes as no surprise this desktop support was the most time consuming element of her job in the early years. With the advent of online GIS, County staff has transitioned most of the towns off of desktop GIS, although there are a small number of towns which still use the desktop client. Most local communities across the County now utilize new AGOL applications. “We often will take the initiative with projects for the towns that relate to work the County Planning Department is doing such as the Warrensburg buildout analysis“, notes Frankenfeld, “as well advocating the adoption of Field Maps for maintaining water and sewer data.”
New GIS Hub
As noted previously, the new Warren County GIS Hub contains three main areas of content: Web Maps and Apps | Maps for Print | Download Data. Each area is then broken down further thematically into categories such as recreation, environment, transportation and infrastructure, planning and zoning, history, citizen reports and more. With an established user community in County government, most of the time departments and organizations now approach GIS staff directly with applications to develop to support their business needs such as the Safe Pace, Opioid Dashboard, Storm Reporter, TIP viewer, etc). Other projects have been initiated by GIS staff themselves such as the covid hub and election polling locator. GIS staff work frequently with other Planning Department and and apply grant funding to create projects such as History Mapper and the letterboxing challenges (Letterboxing Trail and Historians’ Challenge).
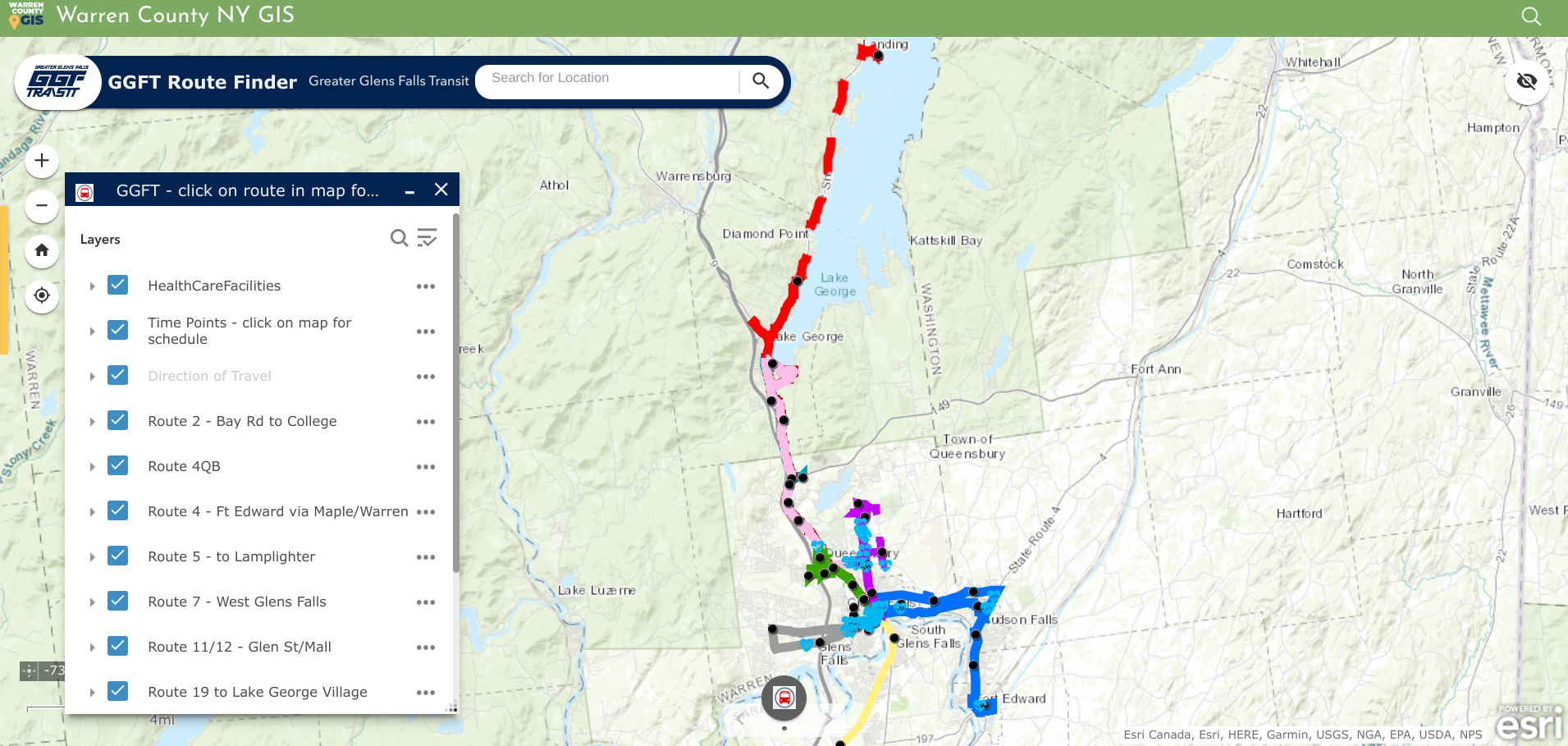
Geospatial viewers are excellent for publishing public transportation systems content. In addition to making time tables and schedules available, ones such as the GGFT also include important public sites such as health care facilities.
Today the COVID Hub is the most popular app though much simplified from early COVID and no longer maintained by the GIS team. It’s had around 1.5 million views since its inception in April 2020 – not bad for a county with a population of 64,000 The next most popular is the parcel viewer app (Community Map), which gets about 12k views a month. After that, the First Wilderness website (about 7k views a month) and the Recreation Mapper which gets a couple hundred views a day, higher in the summer. Warren County’s primary industry is tourism and is an outdoor recreation destination, so trail maps and recreational resources are popular content and Sara and Amanda spend a substantial amount of time creating and maintaining recreation data and providing access to it.
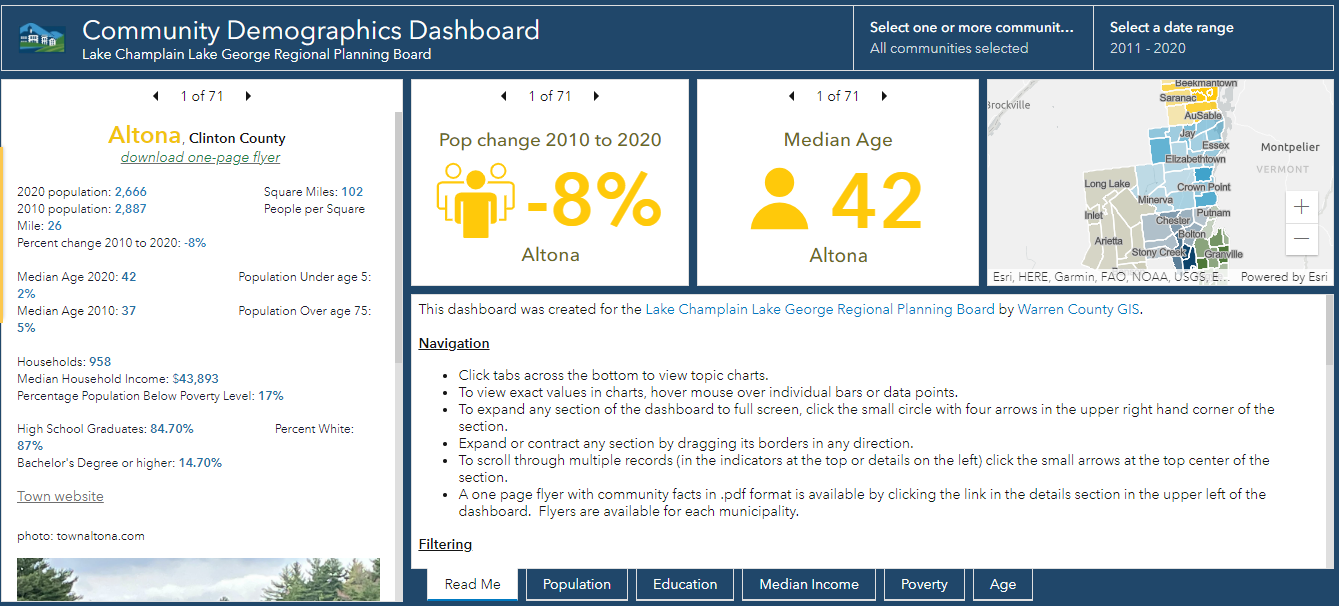
Warren County GIS provides technical support to the Lake Champlain Lake George Regional Planning Board which extends beyond the Warren County footprint. This viewer contains both American Community Survey and 2020 Census data for areas in the five north country counties covered by the Regional Planning Board
Though the application was closed in August, another public facing app focused on the American Recovery Plan Act (ARPA). Survey123 was customized to create an application for those organizations interested in applying for ARPA funding. The applications were made available to committee members for review through a Dashboard, and scoring was completed using another Survey123 form.
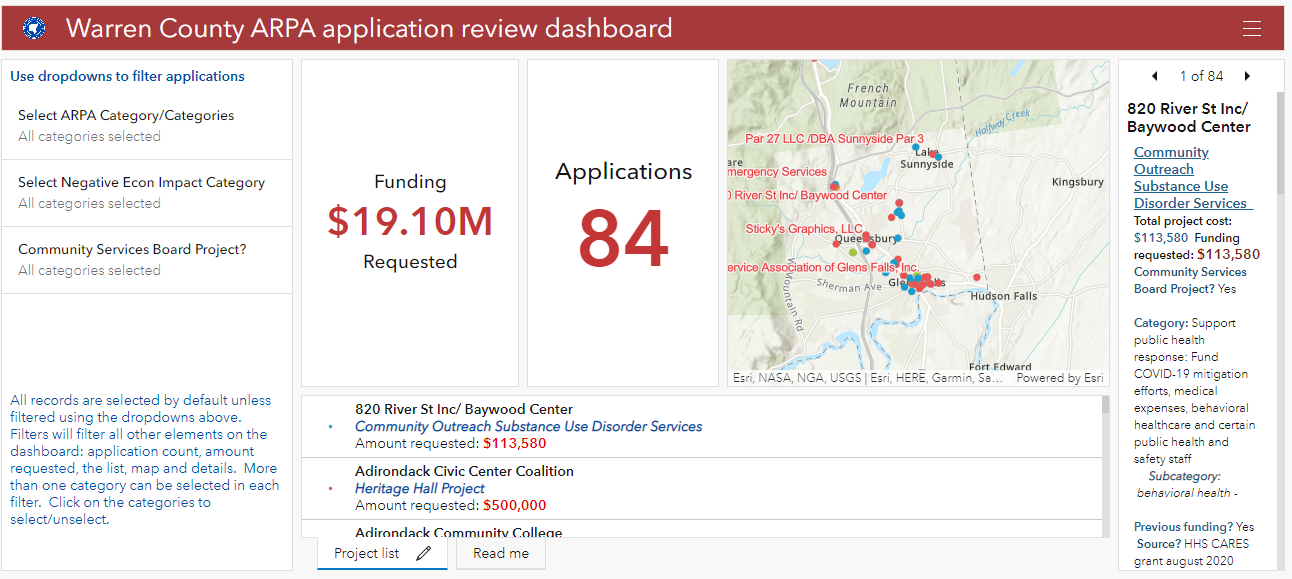
American Recovery Plan Act (ARPA) grant monies provides funding for investment in a wide ranges of community programs and services including geospatial efforts in the rehabilitation and mapping of infrastructure systems.
Sara’s Law
There probably aren’t many geospatial professionals working today across the Empire State that are familiar with Sara’s own little piece of New York State GIS history. The year was 2002 and it was during her first stint with Warren County. While using a GPS unit to map the locations of fire hydrants in the North Creek area, she was “challenged” by the professional surveying community of mapping features in a manner/way she was not qualified to do so. Her post to New York State GIS listserve at the time describing the events read:
“In January, I(Sara) was contacted by an investigator from the New York State Education Department’s Office of Professional Discipline. They had received a complaint from a surveyor stating that I was surveying without a license. I was using a Trimble Pathfinder Pro XR GPS unit to collect fire hydrant locations and then plot them on a reference map. Two investigators met with myself, our planning director, and our county attorney. The investigators were unfamiliar with GPS and GIS and were basically on a fact-finding mission. The investigation has progressed, and today we met with the two investigators, an attorney from the Office for Professional Discipline and a surveyor from the New York State Board of Licensed Engineers and Land Surveyors. The state’s attorney told us at the beginning of the meeting that after reviewing the facts in the case, they do feel that we are guilty of practicing surveying without a license. She then gave our county attorney a chance to state our case, which I thought he did very well. We were informed that the board will make a decision within the next week.”
At the time, it WAS a really big deal in the statewide geospatial and surveying communities – particularly New York State Association of Professional Land Surveyors (NYSAPLS) and the subject of much discussion and debate. Significant in that it marked, for the first time, the visible intersection of emerging GIS/geospatial technologies and the professional discipline of surveying – and by extension, engineering in New York State. While legislation (A01927 & S04396) was proposed in the 2007/2008 timeframe looking to “enhance the definition of land surveying with current standards and tools, i.e., GPS”, nothing was ultimately passed. And along the way over the course of several years, the discussion and the proposed legislation became known as “Sara’s Law”.
Little did she know the backpack GPS unit she was using in 2001 in North Creek would one day be the beginning of bringing these different, but similar geospatial technologies together as they are today. Sara’s place in NYS GIS lore is secure.
Summary
In addition to the broad presence the Warren County GIS program has throughout county government, it also represents the great relationship and guidance county geospatial programs can provide and offer to local governments. Local governments that often have both limited financial and technical resources can benefit greatly from county GIS which have technical expertise and infrastructure in place. A model that can be replicated in other areas across New York State.
Contact
Sara Frankenfeld
GIS Administrator
Warren County GIS
Warren County Municipal Building
Lake George, NY 12845
frankenfelds@warrencountyny.gov
518-761-6410