Some barriers instead might be considered missed opportunities but there continues to be specific issues which stifle geospatial growth
Over my 30+ years of managing the Westchester County GIS program, I worked extensively with local governments across the County. Forty-three in all, ranging from Yonkers, now the third largest city in New York State to several villages which are little more than one-square mile in size such as Buchanan along the Hudson River with a population of 2,302 (2020 Census). All uniquely different in their attempts – and interests – to build geospatial capacity. Some have been successful while many others have struggled for a myriad of reasons. This is particularly true among the 23 villages.
Now “on the other side of the firewall” (thanks, Sue Knauss) and working for myself, I’ve been able to see and work further into the organizational framework of these smaller governments. Confirming many of the observations I made while working with Westchester County that I believe inhibit the development of building geospatial programs at this level of government. Admittedly, the small Westchester County village just north of the Bronx is different in many ways from a small village in Chemung County and one could argue the sample size is too small to be reflective of the entire state of New York, but I would suggest these obstacles to geospatial development are conceptually very similar across the state. Furthermore, the term “Village” is not necessarily synonymous with small government as the Village of Port Chester 2020 population here in Westchester County was 31,581 – larger than many towns across the state. So as a point of reference for this article small governments generally mean those with a population of less than 5,000. Plus or minus.
GIS implementation “how-to” articles, management and primer books, and cautionary experiences shared by software vendors and consultants often include recognized issues such as budget constraints, limited technical expertise, or the lack of a realistic, phased implementation plan, as major culprits in initiating geospatial efforts. I experienced and witnessed many of these same reasons, though the following are five specific barriers which I believe have a major impact in building GIS programs in small governments across New York State.
In no particular order:
- Staff Continuity: On the urban fringes, professional staff, particularly in the front offices, turn over at an amazing rate. Assistants to Village Administrators, Managers, and department heads/commissioners – those who are often tasked to coordinate or serve as a liaison to special projects covering several departments such as GIS implementation – are often on the move. And it’s not just in the administrative offices where staff turnover is impactful, but also throughout key program offices and departments which touch on GIS implementation such as planning, assessment, public works, and water departments, among others. Any successful GIS Manager will tell you one of the most important factors in building the program, or any new government initiative, is staff continuity. Including those who are in charge of managing consultants involved in helping build the GIS program. Losses in these areas are often a major setback and derail any progress that may have been made in the GIS effort. In some cases, losing years of work. It doesn’t matter how good the implementation plan was or the technology being deployed.
2. IT Support: Many small governments often do not have full-time IT staff and normally contract out for this support. And with it, much of the focus is on infrastructure items such as the network, desktop and peripheral hardware components, client software installations/upgrades and as is the case in all governments and businesses now – maintaining the firewall and supporting cyber security efforts. These contracts, which are often with smaller IT firms, rarely include the support or guidance on multi-department applications such as geospatial programs which increasingly include mobile applications and its peripheral components. This is not to say smaller IT firms cannot support GIS, it’s just not normally in their wheelhouse. In small governments, needed GIS support from IT resources for a “government-wide perspective” is often extremely limited.
3. Software Application Silos: In small governments where there is often an absence of an overarching “IT committee” and/or the like, as well as combined with the lack of full-time IT staff as noted above, it is not uncommon for individual departments to be left to themselves to make their own business software decisions. And as software vendors continue to push for and offer cloud-based/browser only solutions for their software products, it is even easier for individual departments and programs to go rogue and operate further in obscurity from the primary or seemingly “adopted” computing environments in the organization. In fact, it’s not uncommon for IT support in small governments (I’ve even seen this at the City level) to not even know what browser-based business solutions some departments are using on a day-to-day basis.
What makes this difficult in the GIS space is that practically all business software solutions now include some kind of “mapping” component – if only to render the application data on some form of generic base map. Most often Google Maps. Often the user interface even includes the term “GIS” when simply viewing program data on a map – this being the extent of the “GIS” functionality. And if and when the broader discussion of a GIS for the government is ever started, these same departments are slow, if ever, to join the effort. Not knowing the larger intricacies and benefits of a shared, multi-department GIS program – the response is normally “We already have a GIS“. Little interest in the shared data model, to say the least of a common address file which most business software products normally ship to support geocoding. This cloud-only software application delivery model (mobile apps, too) is very common now in local government permitting, code enforcement, inspections, and even public safety disciplines to name just a few.
If it’s not broken, they are not going to try and fix it. Let alone spend more money. Making it very difficult to garner interest for a government-wide discussion on a unified GIS solution.
4. VIPs with an Attitude: That may sound a little harsh, but the fact of the matter is that just one dominant personality in small governments can impact the decision making process over a wide range of internal technology issues – not just GIS. Such individuals exist in all levels of government, but in smaller ones, where staff are few in numbers and VIPs normally being senior staffers – frequently with decades of service – his or her opinion is often unquestioned. Your first onsite meeting with folks who are genuinely interested in the GIS goes well – that’s why you’re there in the first place. But during the second or third on-site meeting which is held to take a deeper dive into the concept – the VIP with an Attitude shows up out of nowhere acting like Lord Vadar. Often packing a lightsaber.
Because of their decades of institutional knowledge, they have been ordained to know what is best for the good of the order. Even if he or she isn’t even directly involved in geospatial. Like a good defense lawyer, raising just an iota of doubt on what is deemed such a good idea by so many others.
Magically the VIPs have the ear of the Budget Director, Comptroller, Finance Director, fellow high ranking directors, or highest elected official. Or the Town Board. And so forth. Across the municipal landscape they can be found in one of many program areas: Public Works, Finance, Building Department, maybe a small Planning office, or even a long standing consultant who isn’t even on the payroll. For whatever reason, he or she feels threatened by the technology which is being considered and increasingly adopted elsewhere. Particularly if the VIP has not taken the time to understand the benefits that geospatial programs can bring.
But it’s not going to happen while they are still around and/or have something to say about it. In my hometown, early GIS efforts were thwarted by the Receiver of Taxes. Yes, Receiver of Taxes. Largely because this office was responsible for “computer related” expenditures. And nothing was going to compromise his/her annual computer software and hardware needs. To this day, the program has never gotten on track.
There is really no good solution for the VIP with an Attitude problem in small governments. Sometimes retirement and attrition takes care of the problem though this may take years. A change in administration sometimes helps, but in small governments new administrators rarely question long standing, senior staff members. If anything they embrace the input and advice of VIPers.
And the beat goes on.
5, Consulting Engineers: Small governments often do not have a professional engineer on staff and normally contract out needed engineering services. Engineering firms, whether small or large, which secure these services can have a profound impact on the use and development of GIS in small governments. Though many small governments today do not see or consider their consulting engineers in this capacity. Most aren’t even aware of the possible connection.
Back in the day of desktop/client GIS solutions, such support by consulting engineers was unrealistic. But now, with easy-to-use cloud-based offerings such as ArcGIS Online, consulting engineers, along with their arsenal of AutoCAD related products and technologies, can simply envelope this “GIS service” into annual support services contracts. At many levels of government, and particularly true in smaller ones, consulting engineers come in contact with all types of municipal geospatial data. While infrastructure data (storm, sanitary, water distribution systems) are often the most obvious, consulting engineers duties also often include staffing local Planning Boards, serving as a liaison to utilities and a myriad of regional, state, and federal programs which include geospatial connections, as well as being involved in a host of local surveying and land/property record issues. Depending on the in-house GIS resource capacity the consulting engineer maintains and the licensing agreement with the software vendor, consulting engineers can offer a range of GIS capabilities to get small governments started for minimal investments.
The reasons are many why this connection is not more common, but this “barrier” is more of a business relationship that more small governments should try and leverage with their consulting engineers. There are positive and long term benefits for each party.
Summary
At the end of the day, yes, the scale of small government operations and the scope of the geographical area covered may not seem to justify the investment in a comprehensive geospatial program. Leading to a perception among the local elected officials, perhaps even department heads, that the benefits may not outweigh the costs. Though the path I took in and out local government buildings, a basic lack of education and awareness of the geospatial benefits was still always an issue. Particularly among the highest elected official and governing boards. But it doesn’t stop there as I believe there still continues to be a significant lack of awareness or understanding of the broad spectrum of geospatial technologies among elected state representatives as well.
For years, I’ve passively monitored the websites of New York State Association of Towns and New York Conference of Mayors as a source of ideas for articles for this blog. Both organizations represent elected officials (including council members, boards, clerks and other municipal staff members as well) and are an excellent source of advocacy for small government programs and funding where geospatial technologies can be applied (i.e., transportation, infrastructure, public safety, environmental protection, etc). Even New York State Association of Counties (NYSAC) for the most rural of our state counties serves in this capacity as well. If one takes the time to drive around and research each of the association websites, including using key word search tools, there is little reference to GIS or geospatial technologies. Or for that matter, little of the technologies that geospatial is wrapped into.
These organizations would be an excellent source of geospatial awareness at their newly elected training programs or annual conferences – which are extensive. Helping connect geospatial to the programs they fund and how the tools are applied locally. (For this article I looked for similar training sessions for newly elected New York Assembly members but could not find any specific programs). Perhaps an opportunity for organizations like the NYS GIS Association or our emerging academic programs to provide training session/seminars to these associations.
There will continue to be exceptions, but until the opportunities and awareness of geospatial technologies are better understood, small government GIS programs in New York State will continue to struggle.









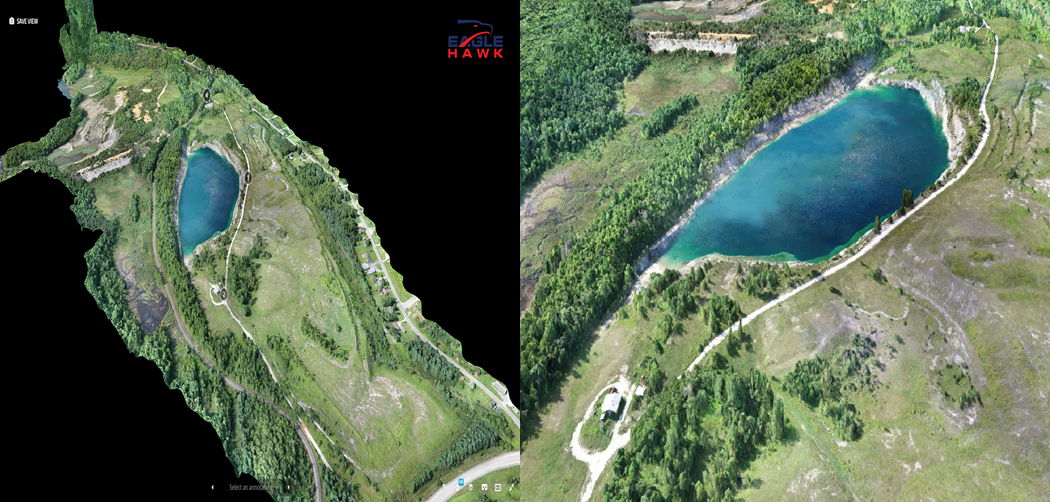
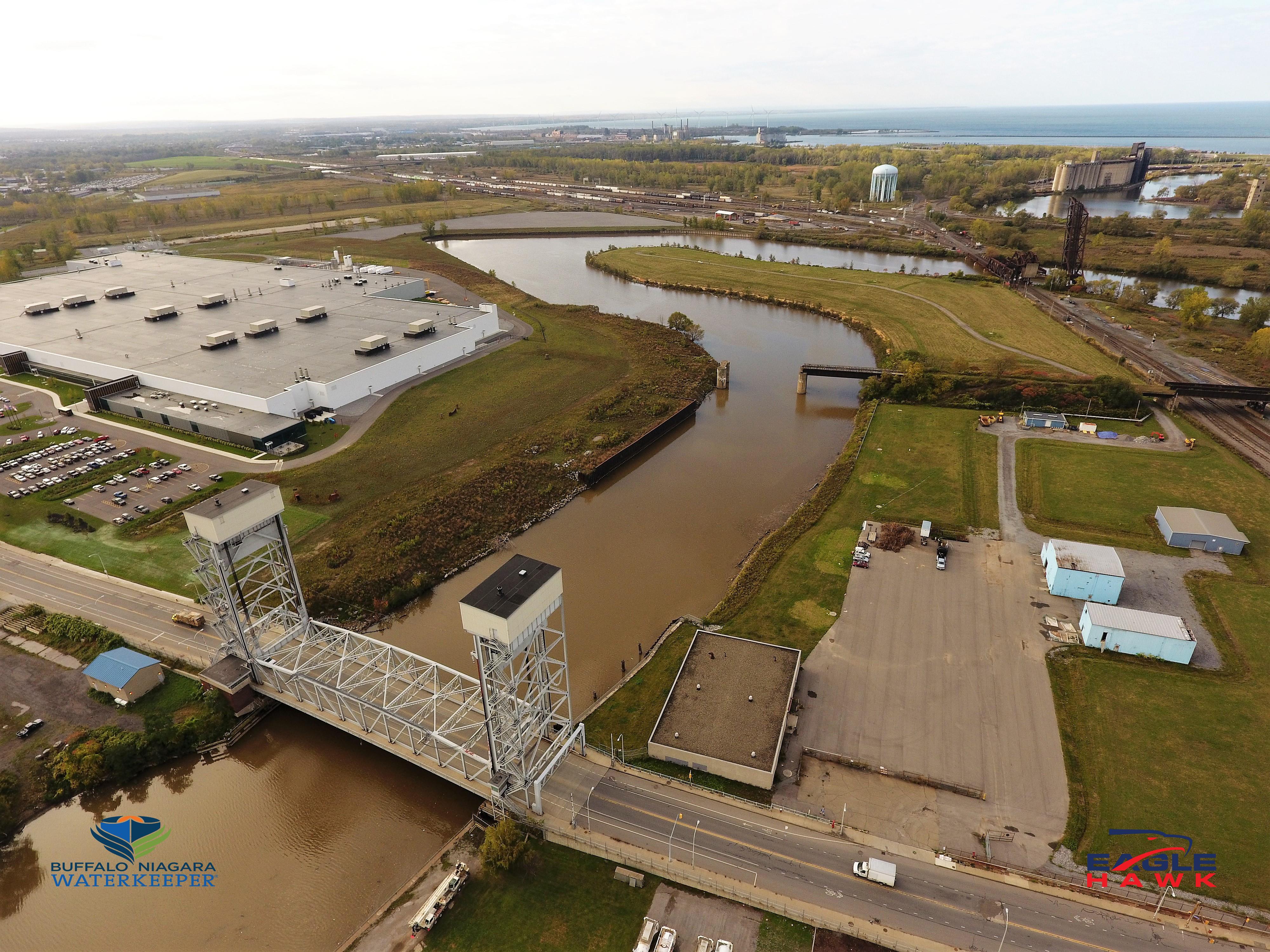
 EagleHawk was founded in 2016 by
EagleHawk was founded in 2016 by 


 eSpatiallyNewYork: You work in both Madison (Hamilton) and Chenango (Sherburne and North Norwich) Counties. When did you begin to see computer mapping and technology changes in your offices?
eSpatiallyNewYork: You work in both Madison (Hamilton) and Chenango (Sherburne and North Norwich) Counties. When did you begin to see computer mapping and technology changes in your offices?