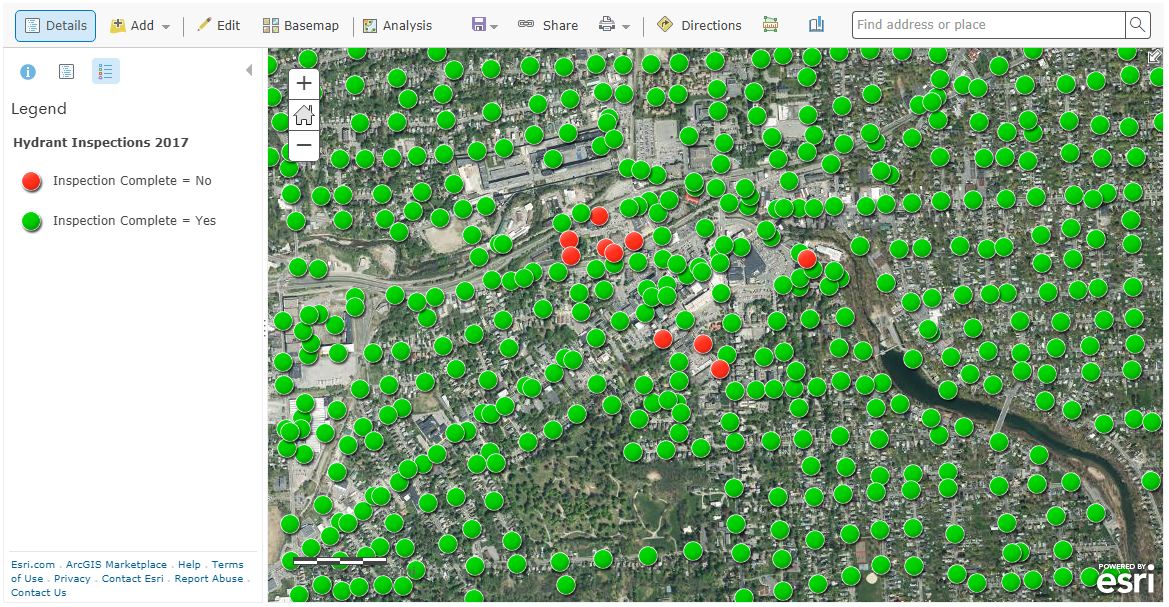
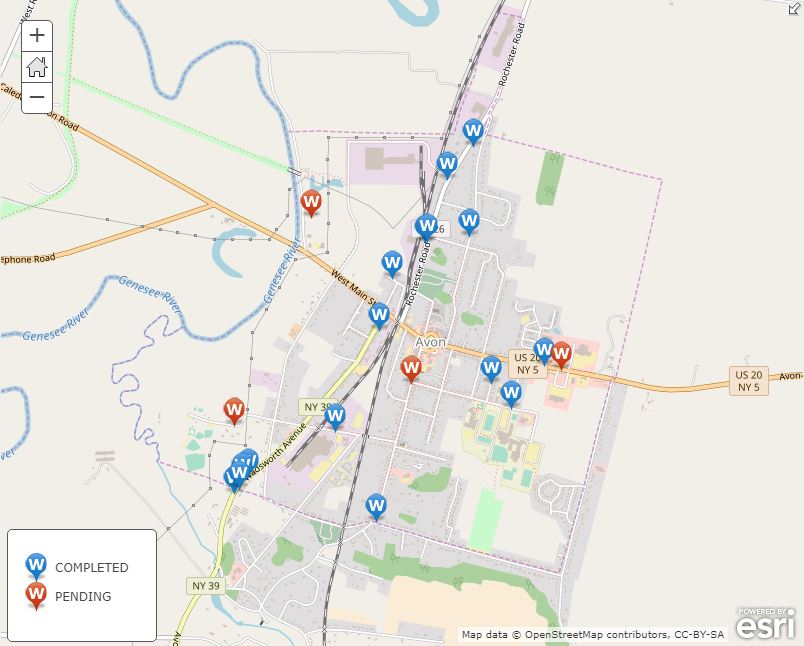
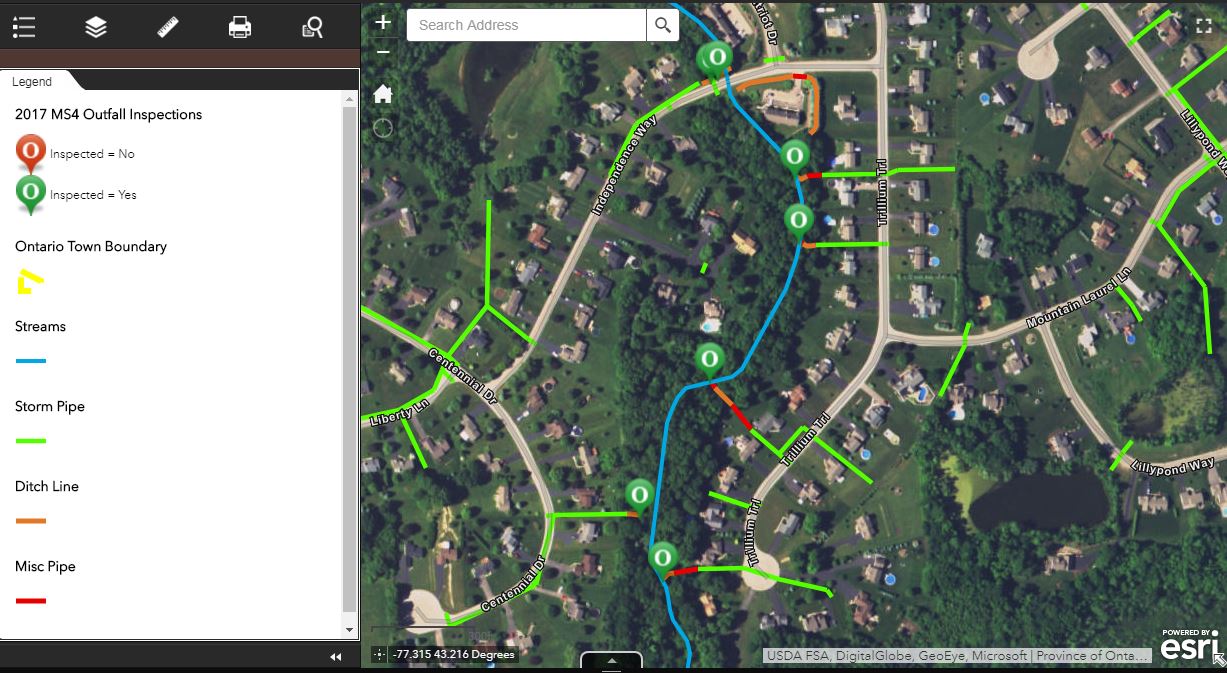
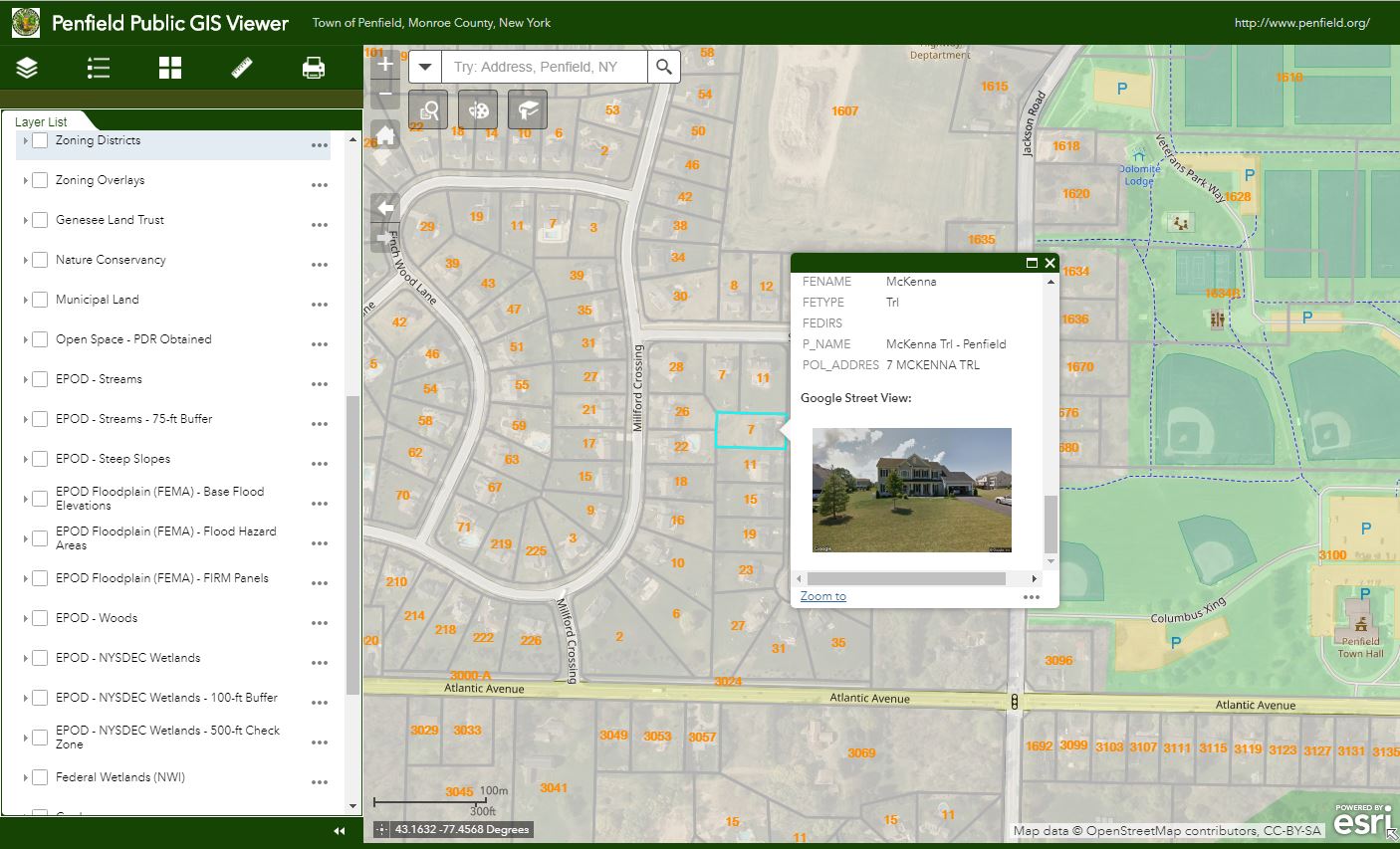
Making it the largest annual event to date, nearly 200 individuals attended the 2019 Westchester GIS User Group Meeting May 16th at Purchase College. The annual event included a diverse mixture of user presentations and demonstrations for attendees representing local and county government, utilities, nonprofits, business and industry, and academia (both college and high school programs). Faculty and facility support from the College’s Environmental Studies program and sponsorship from twelve vendors again helped enable the Westchester County GIS community to meet and discuss the countywide geospatial agenda. And by virtue of the venue, promoting SUNY GIS educational opportunities as well. It was a great GIS day for all attending and participating.

As the day progressed, nearly 200 registrants assembled as part of the 2019 Westchester GIS User Group Meeting at Purchase College. The main lecture auditorium was filled to capacity with standing room only by mid-morning.
2019 Agenda and Speakers
While the 2018 agenda had a specific theme, this year’s agenda was intended to be more diverse covering a wide range of topics including health and human services, pavement management systems, oblique imagery applications, training workshops, forestry inventories, public safety, mapping and visualizing the human brain, the 2020 Census, and a special presentation by ESRI focusing on accessing the County’s new planimetric datasets via web services.
Session I: Allison McSpedon and Jeff Worden from the Westchester County Continuum of Care Partnership for the Homeless led the day off with a presentation focusing on the use of mobile technology as part of the annual Homeless Point in Time (PIT) Count taken in January 2019. This was followed by Nancy Birnbaum, Manager of Software Architecture, Westchester County Dept. of Information Technology who presented the new Westchester County Online Community Mental Health Directory.

Managers from the Continuum of Care Partnership for the Homeless detailed the pros and cons on the use of mobile data collection technology as part of the January 2019 count. They anticipate even better results and ease of use when deployed in the next count.
Andrew Reinmann, Advanced Science Research Center, Graduate Center of CUNY and Department of Geography, Hunter College followed with the use of geospatial tools as part of the Westchester County Forestry Inventory: Mapping and Ecosystem Services Assessment. The morning session ended with a series of lightning talks highlighting the use of the County’s new oblique imagery.
Session II: After intermission, VHB and staff from Westchester County Dept. of Public Works and Transportation discussed the new Smart Asset Management and Inventory System (SAMIS) application which was followed by an excellent demonstration on the use of Laser Scanning technology by the Westchester County Police Forensic Investigations Unit. Patrick Gahagan, Technical Analyst at ESRI finished the morning session discussing advancements in civil engineering and surveying integration between the Autodesk and ESRI platforms.

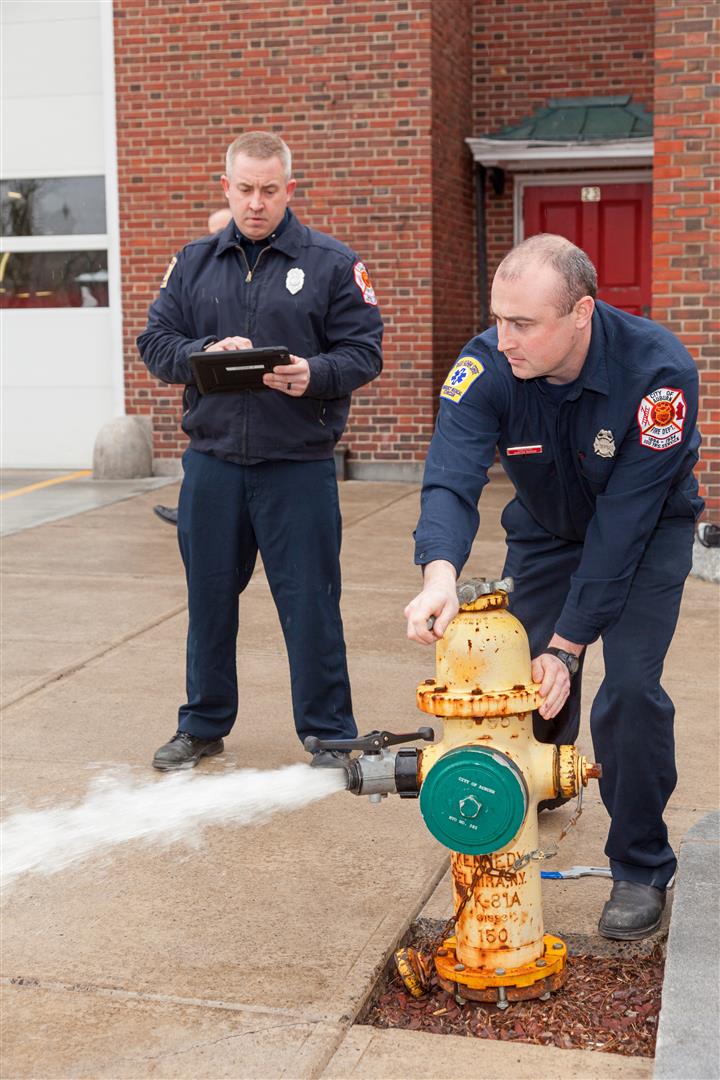
Detectives from the County Police Forensic Unit captivated the audience on the use of laser scanning in crime scene investigations. GIS staff is now working with the Forensic Unit on integrating laser scanning data into the enterprise GIS environment.
Session III: After lunch – and an audience participation session of GeoJeopardy – Jonathan A. N. Fisher, Ph.D., Director of the nearby Neurosensory Engineering Lab at the New York Medical College in Valhalla provided an overview of his project called Neurodome which centers on the mapping of the human brain with an assortment of technology and visualization tools. Daniel Wickens, Solution Engineer from ESRI then gave two overviews on “What’s New with ArcGIS Field Apps and ArcGIS Online.” Concurrently in separate locations training classes were offered on how to use the new online CONNECTExplorer oblique imagery viewer and the ESRI “Explore Future Climate Change” tutorial.
Session IV: The last section of the agenda was brief and included an update on mapping efforts association with the 2020 Census by Margaret Baker, Geographer, from the U.S. Census Bureau Manhattan office. The final presentation by Westchester County GIS staff included the latest developments and anticipated upgrades to the Westchester County GIS website including the scheduled launch of the Westchester GIS Geospatial Gateway
Individual meeting presentations can be accessed and downloaded using this link.

The U.S. Census Bureau is ramping up for the 2020 Census and has a variety of mapping and geospatial products in their toolbox. GIS technology is essential in helping identify areas which have had low counts and responses.
Little Things Make it Work
I’ve written before about the small details which we believe enable the Annual Westchester GIS User Group Meeting to continue to be successful – and we’re the first to admit there is always the element of luck. Even the weather matters. To the extent possible, elements such as keeping the content and speakers “Westchester” focused, minimal – if any – registration fees, lots of time for interaction with the sponsors on the exhibit floor, and the centrally located venue at Purchase College – all matter. One of the ironies, and downsides, of having the show on a college campus in mid-to-late May is that spring semester is already over and students have fled campus. However, there is normally a handful attending looking for summer or full-time work and passing out resumes. The naturally lighted vendor area in the Natural Sciences Building, albeit small, adds to the personal “feel” of the show. Easy access and plenty of parking is also essential. And don’t forget lots of proactive outreach to the professional organizations and societies we work with on a day-to-day basis: police/fire, engineering, surveying, public works, assessors, nonprofits, and the planning community. The added message here is to encourage consultants which are supporting local governments across the county – to attend the meeting. To learn more about accessing and leveraging Westchester County GIS products and services and how this improves service and cost efficiencies to municipalities they serve. Individually, any of these items listed above may seem trivial, but they all add up in delivering a show that will bring the same people back next year.
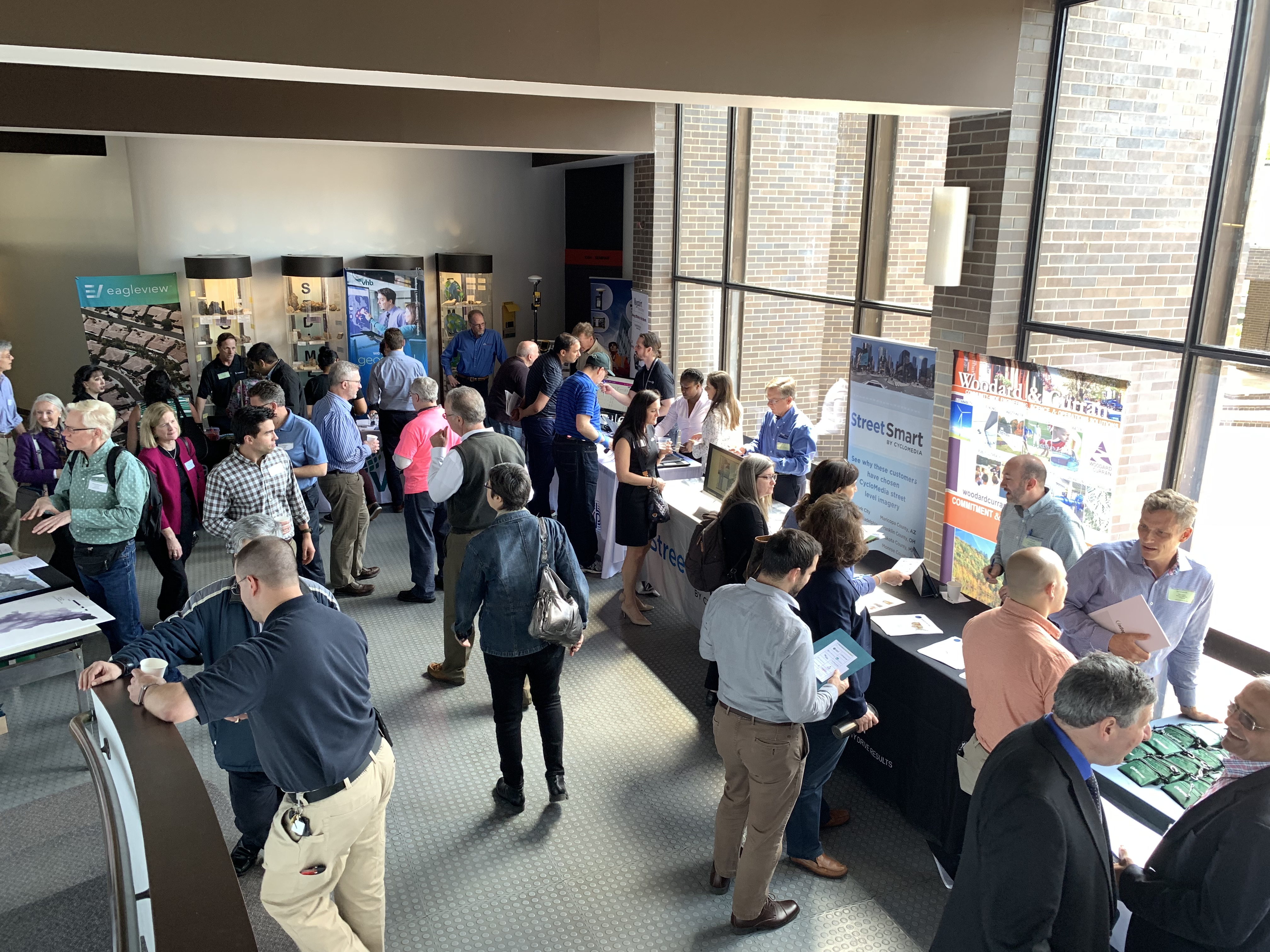

The exhibit floor was busy (and loud!) during breaks with all vendors noting interaction with attendees was good and productive. All attendees can complete a Vendor Bingo Card and be eligible for a raffle prize at the end of the day. This year’s prize was a vendor donated iPad!
Summary
Over the next couple weeks, conference organizers will be sending out a survey to both attendees and vendors to gather more detailed information on the various elements (presentations, speakers, refreshments/breaks, vendor interaction/feedback, facility issues and the like) of the show. This information will help guide decisions about content and any changes that may need to be made, if any, about the structure of the show.
Staff will take a few months off and begin planning for the 2020 show in the fall of this year. In doing so, we look forward to the continued relevance and position of the Westchester GIS User Group Meeting in promoting countywide geospatial development and use.

 eSpatiallyNewYork: You work in both Madison (Hamilton) and Chenango (Sherburne and North Norwich) Counties. When did you begin to see computer mapping and technology changes in your offices?
eSpatiallyNewYork: You work in both Madison (Hamilton) and Chenango (Sherburne and North Norwich) Counties. When did you begin to see computer mapping and technology changes in your offices?
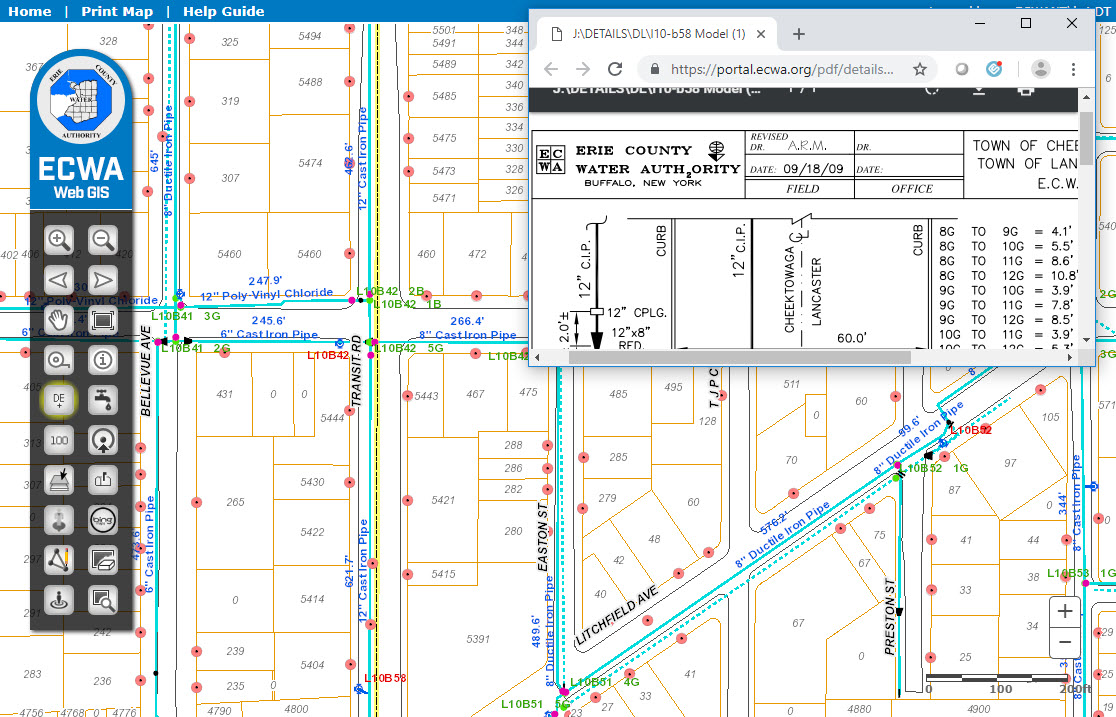
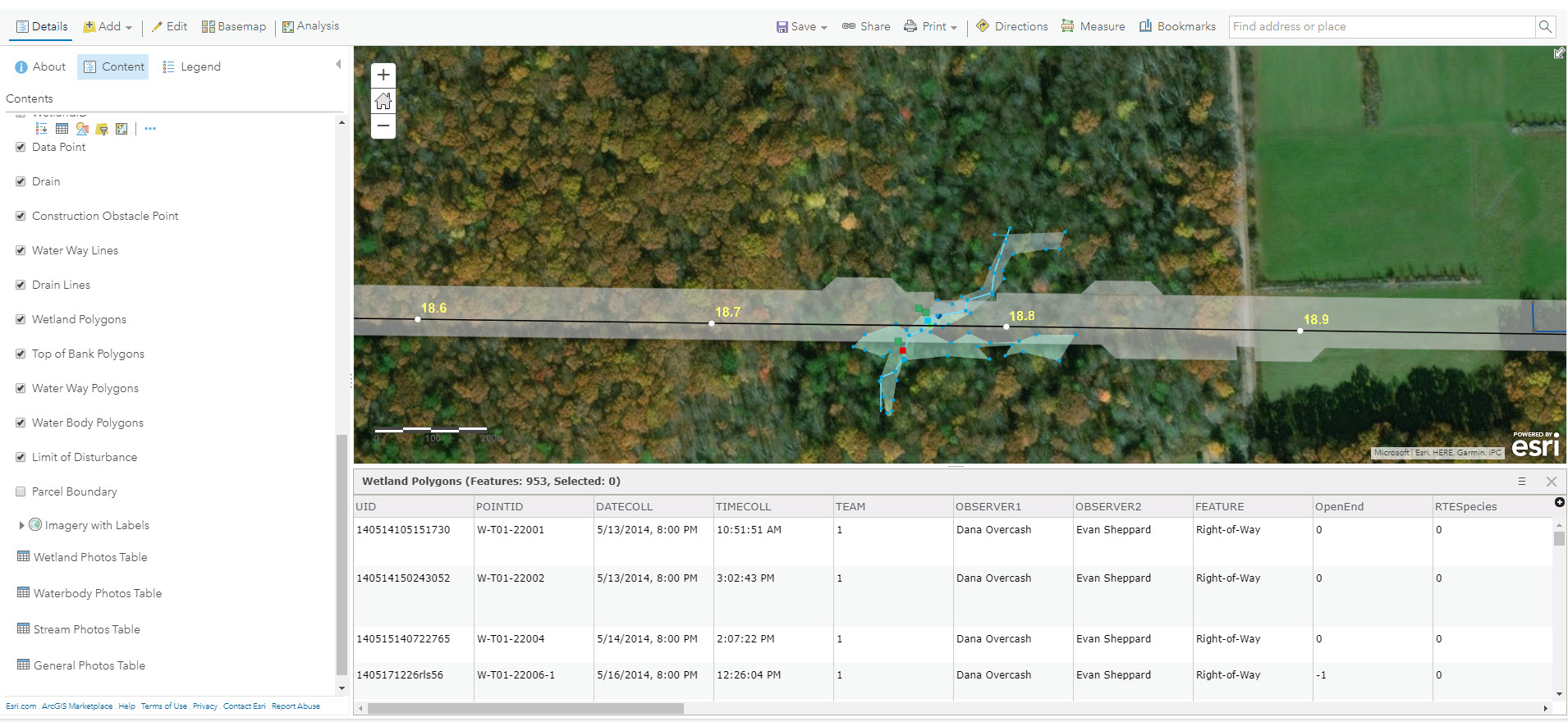
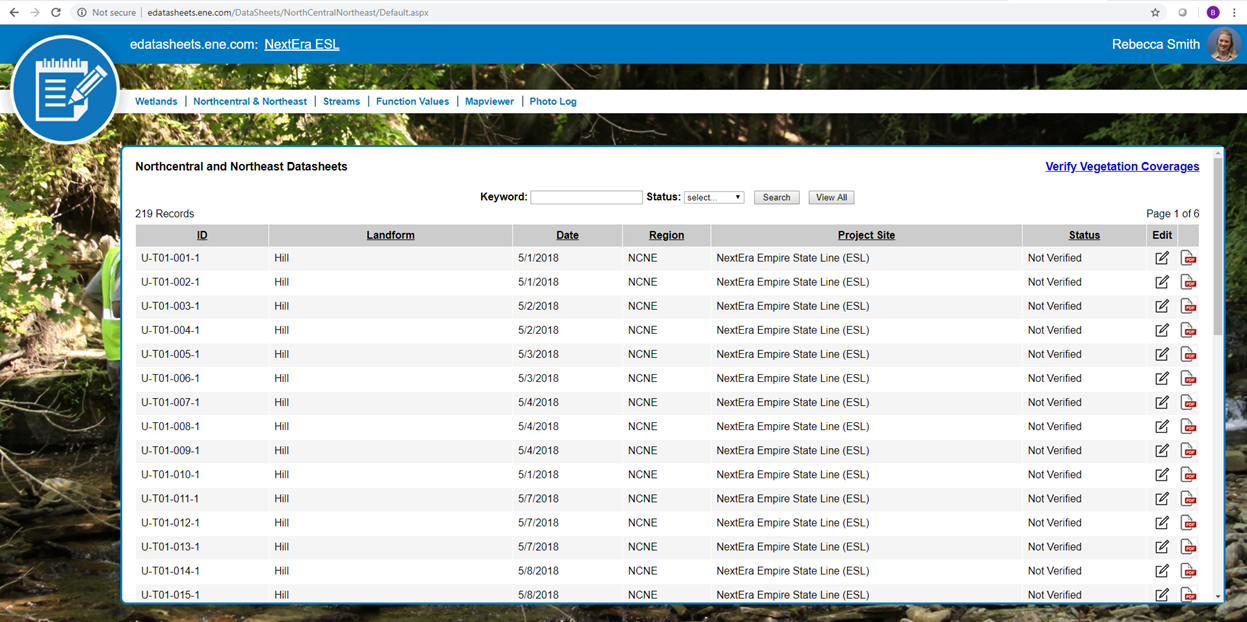


 For many New York State local governments, GIS is not just a flashy map or application. It is a tool to manage vital records focusing on real property, development, and infrastructure.
For many New York State local governments, GIS is not just a flashy map or application. It is a tool to manage vital records focusing on real property, development, and infrastructure.