Company Name: Geocove
Location: Cheektowaga, New York
Employees: 5
Established: 2006
Website: www.geocove.com
The Company

Geocove is an award-winning GIS software and professional services firm established to provide GIS support and technology to local, state and regional government agencies and utilities nationwide.
Founded in 2006, Geocove has been an authorized Esri business partner since 2007. Their team of professionals has decades of experience providing GIS consulting, system support, application development and data collection tools. Geocove, which is led by a former Esri employee, supports the Esri GIS ecosystem with the best-in-class GIS tools, including Esri templates, custom built tools and apps, or other Esri business partner systems.
Geocove’s success is the result of the success of their customers which is achieved by increasing task effectiveness and capabilities using the appropriate GIS technology. Geocove is certified as Disadvantaged Business Enterprise (DBE) by the New York Department of Transportation, and a Woman-Owned Business Enterprise (WBE) by the State of New York, along with several other certifications.
Software & Capabilities
Geocove offers a wide range of GIS Services including:
- Ad Hoc Support
- Utility Network
- Asset Inventory Tools and Solutions
- Parcel Fabric and/or Property Management
- Consultation and Strategic Workshops
- Data Collection Tools
- Data Transformation
- Enterprise GIS Implementation
- Facility Management
- Jumpstarts
- Knowledge Transfers
- Mapping
- Situational Awareness
- Solution Design and Development
- Staff Augmentation
- Sample Products and Applications
Sample Products and Applications
Geocove has a long history of supporting the Town of Tonawanda’s GIS needs from data editing through system design and maintenance. They continue to work as its GIS administrative and support team, and consulting with senior Town staff about continued development of the GIS program.
Their ongoing support expands the Town’s current GIS capabilities and infrastructure by providing software upgrades, managing databases and GIS servers, building web applications, writing custom tools, providing GIS analysis, map production and staff training. Currently Geocove is upgrading the Town to Esri’s 11.4 infrastructure including ArcGIS Server, Portal, Desktops and supporting scripts, data, map documents and web applications.
Geocove continues to leverage and customize Esri solutions for the Town in several program areas. Most recently, Geocove updated the Town’s water, sewer and storm infrastructure within the Town’s enterprise database from various sources including AutoCAD and hand drawn sketches.
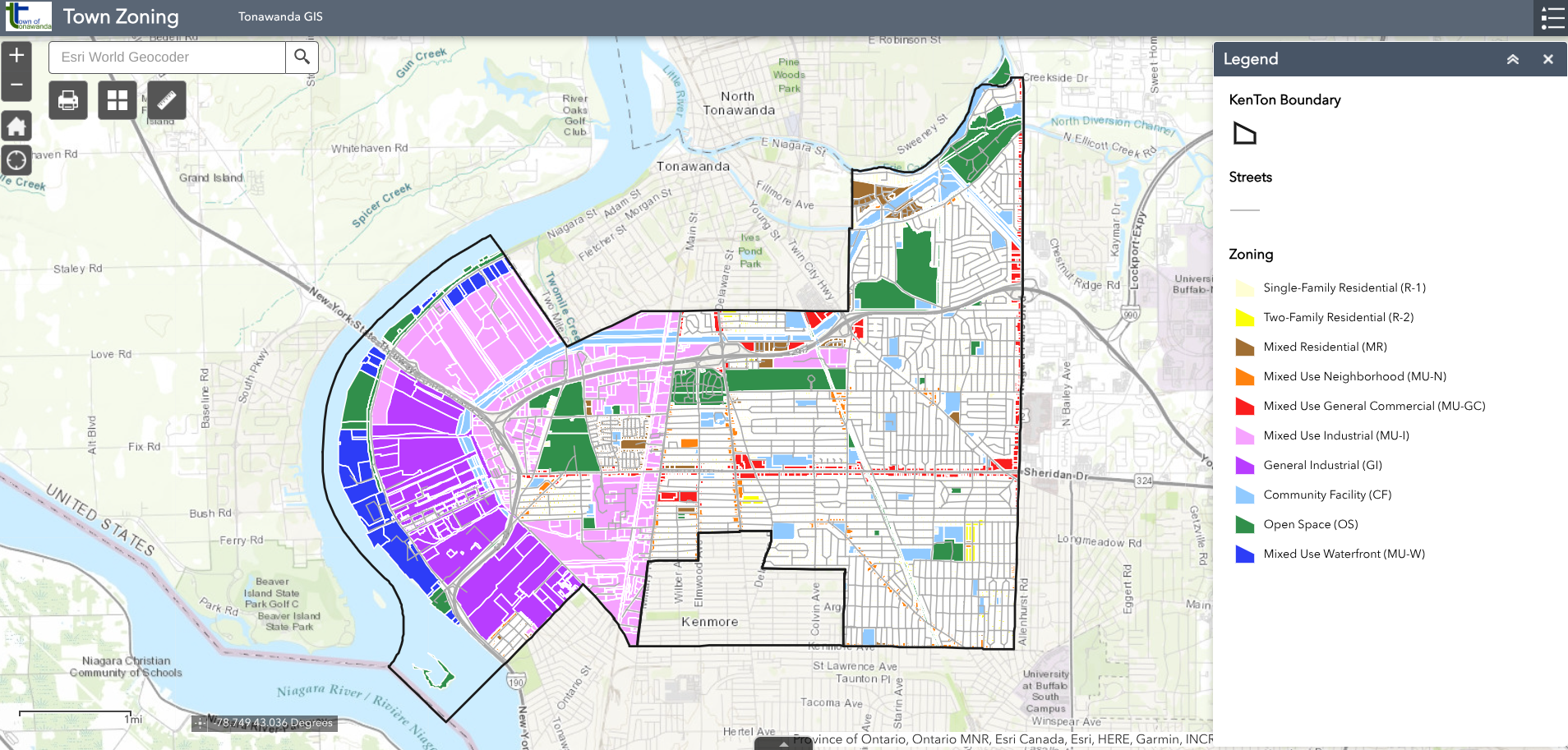
The Town of Tonawanda’s Official Zoning Map was adopted April 9, 2024 and is currently available online as part of the GIS web site.
A project tracking application Geocove created evolved into a project management system. The application has been developed and deployed to multiple departments including highway, engineering and water utilities, ensuring future projects are scheduled appropriately.
Geocove has also worked with the Town to design and deploy Esri-based solutions to identify streetlight fixtures for purchase and to track the conversion project. Those solutions – including out-of-the-box components such as Survey123, ArcGIS dashboards and a web editing application – are now used for operation and management of the new system.
A simple custom tool was created to provide email alerts to both the residents and the internal staff for submissions and status updates as appropriate. By configuring the available and proper out-of-the-box tools to build a system (not a custom application), the Town is enabling easier transitions to future Esri versions.
Geocove built several solutions for the Town’s Highway Department, including apps for sign management, sidewalk and street tree management and public viewing. ADA complaints are tracked through the GIS, from a field inventory of trip hazards to follow-up on future repairs, including identifying, prioritizing and documenting situation status and responsibilities.

The street tree app was one of many developed for the Highway Department and has proven to be useful for both town staff and the general public.
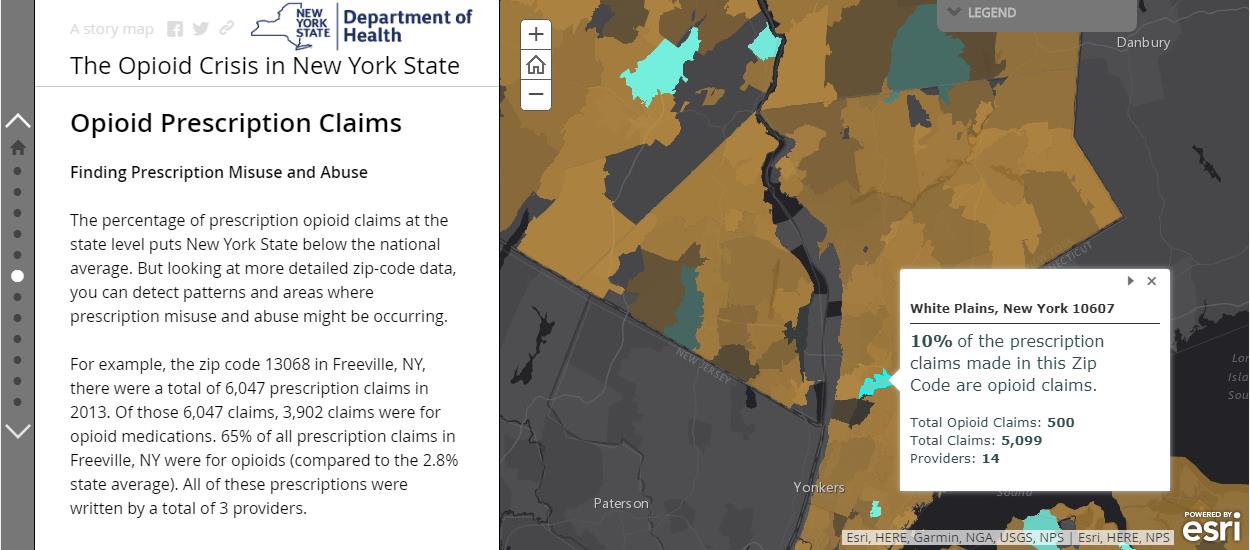
Matt Sutton, Town Engineer, said the maps created with Geocove’s support are available to residents and businesses to access a variety of information: “The tree inventory map gives information [on] Town-owned trees. The details map allows the user to view the tree species, height, diameter, etc. When the forestry department cuts down a tree, this GIS database is updated,” Sutton said, adding: “We were also able to create comparison maps showing aerials of the town from today, through previous years all the way back to 1951.”
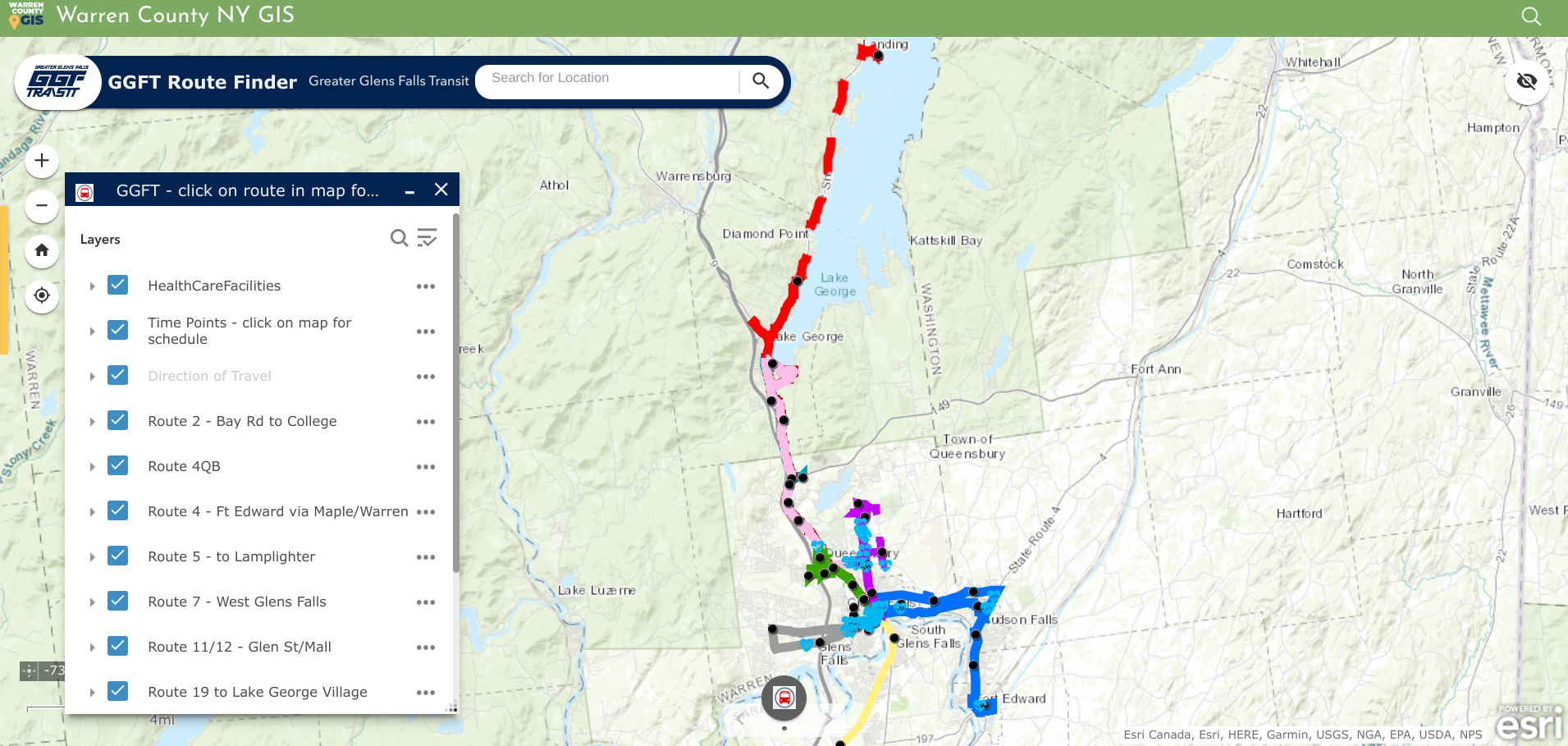
Geocove began working with the Town of Tonawanda in 2015, when they had a handful of apps they supported. The town currently has 271 maps and apps, serving 10 departments, 94 apps are shared publicly. “We are very proud to have built almost all of those,” says Karyn Tareen Geocove President.
In July 2023, the Town of Tonawanda and Geocove’s team was honored to receive a Special Achievement in GIS award from Jack Dangermond at the Esri International User Conference.
Geocove’s first Livingston County project was with its Planning, ITS and Real Property Tax Services departments. Each identified unmet geospatial needs in their departments and others within the county.
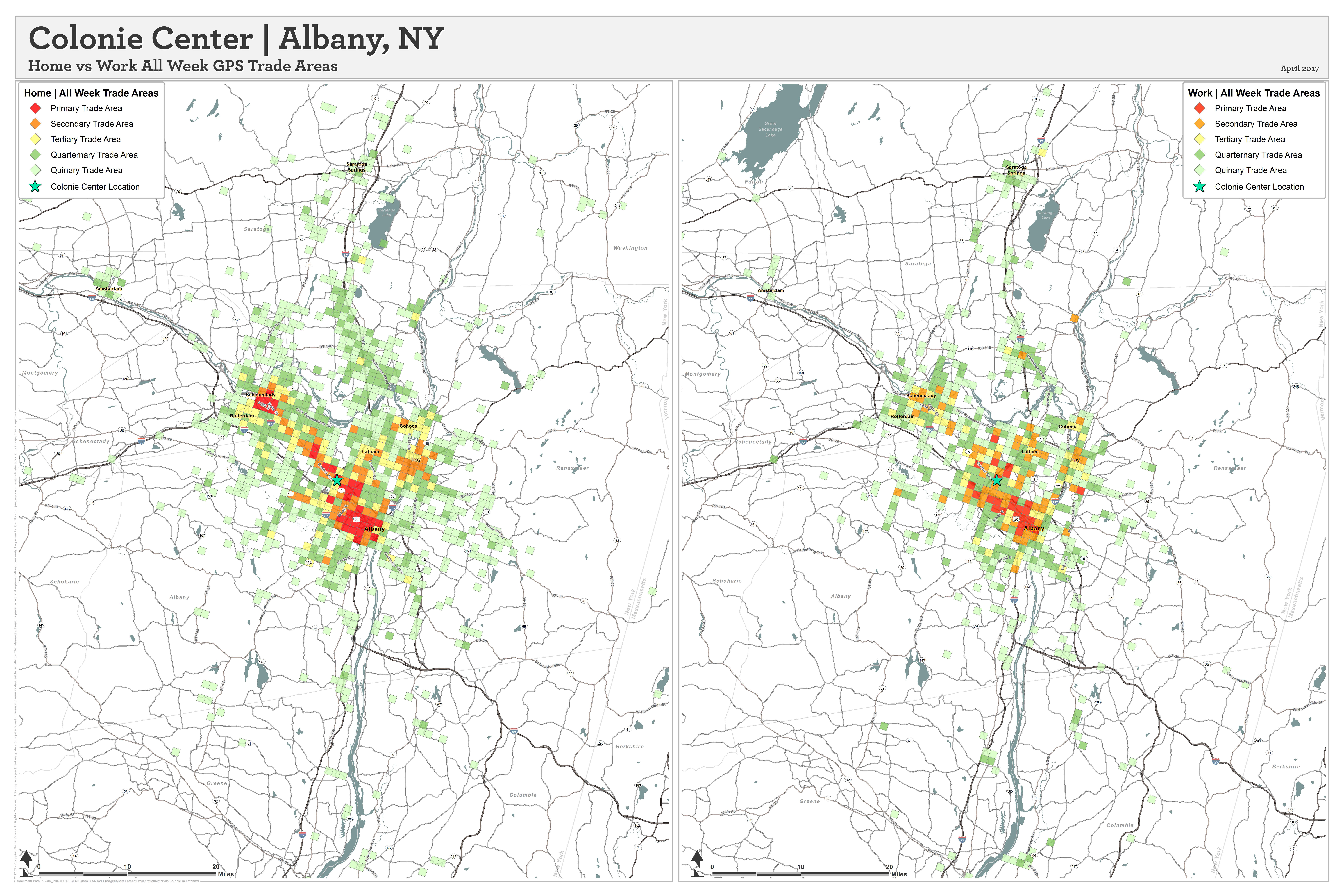
Geocove was then hired as the County’s GIS advisor and to perform specific tasks, including establishing a publicly accessible GIS portal and updating the county’s public map. Through repetitive GIS project and ad hoc support contracts, Geocove has upgraded the County’s GIS software several times. By providing recommendations, design and implementation services they upgraded Livingston County to a new Enterprise GIS architecture and helped the county to migrate existing tools, applications and users to the new environment.
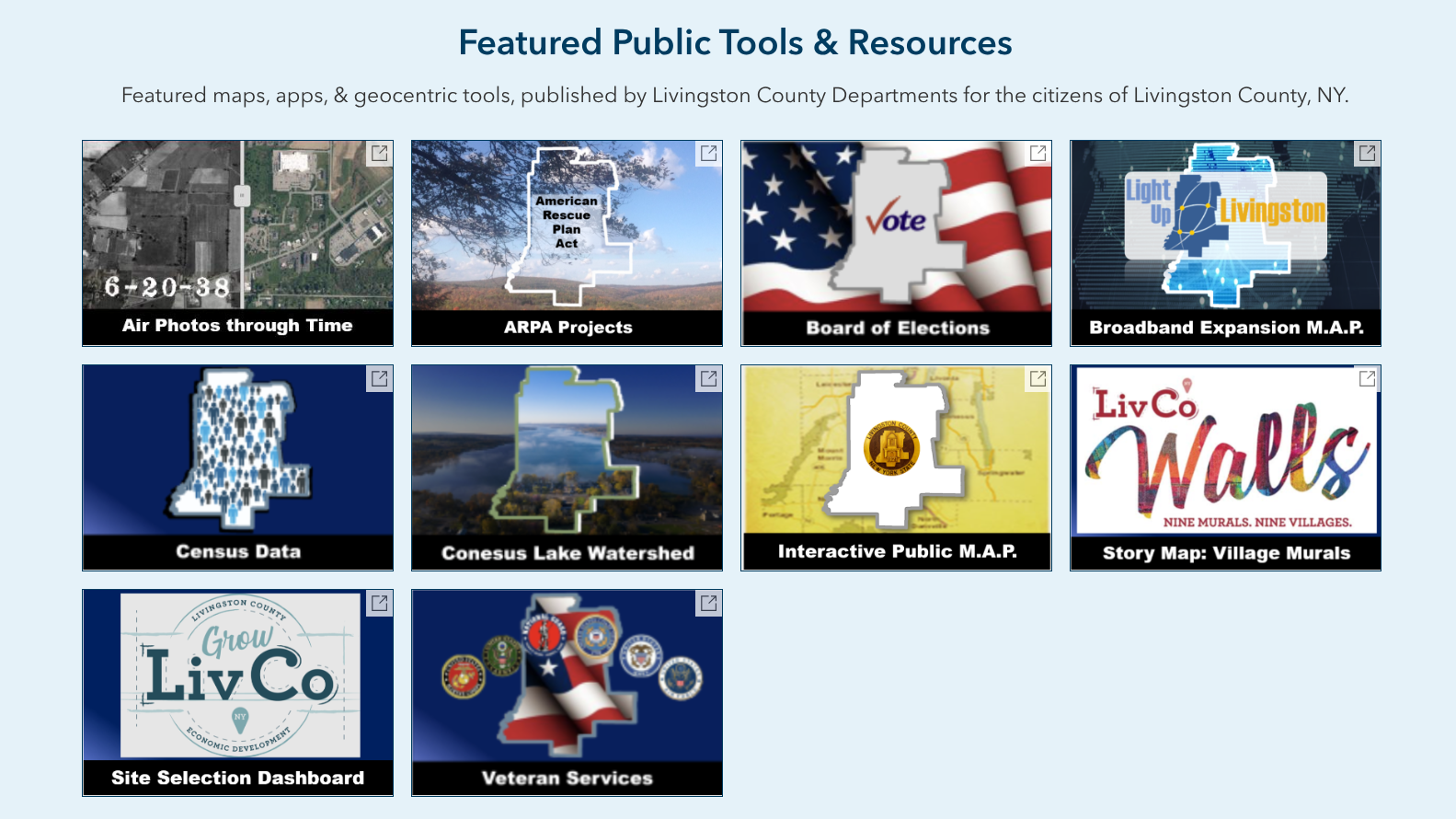
Before Geocove, Livingston County had only one app functioning. Based on Geocove’s work to date, the County now has 112 maps and apps, with focused apps for 11 departments and 26 public facing GIS applications.
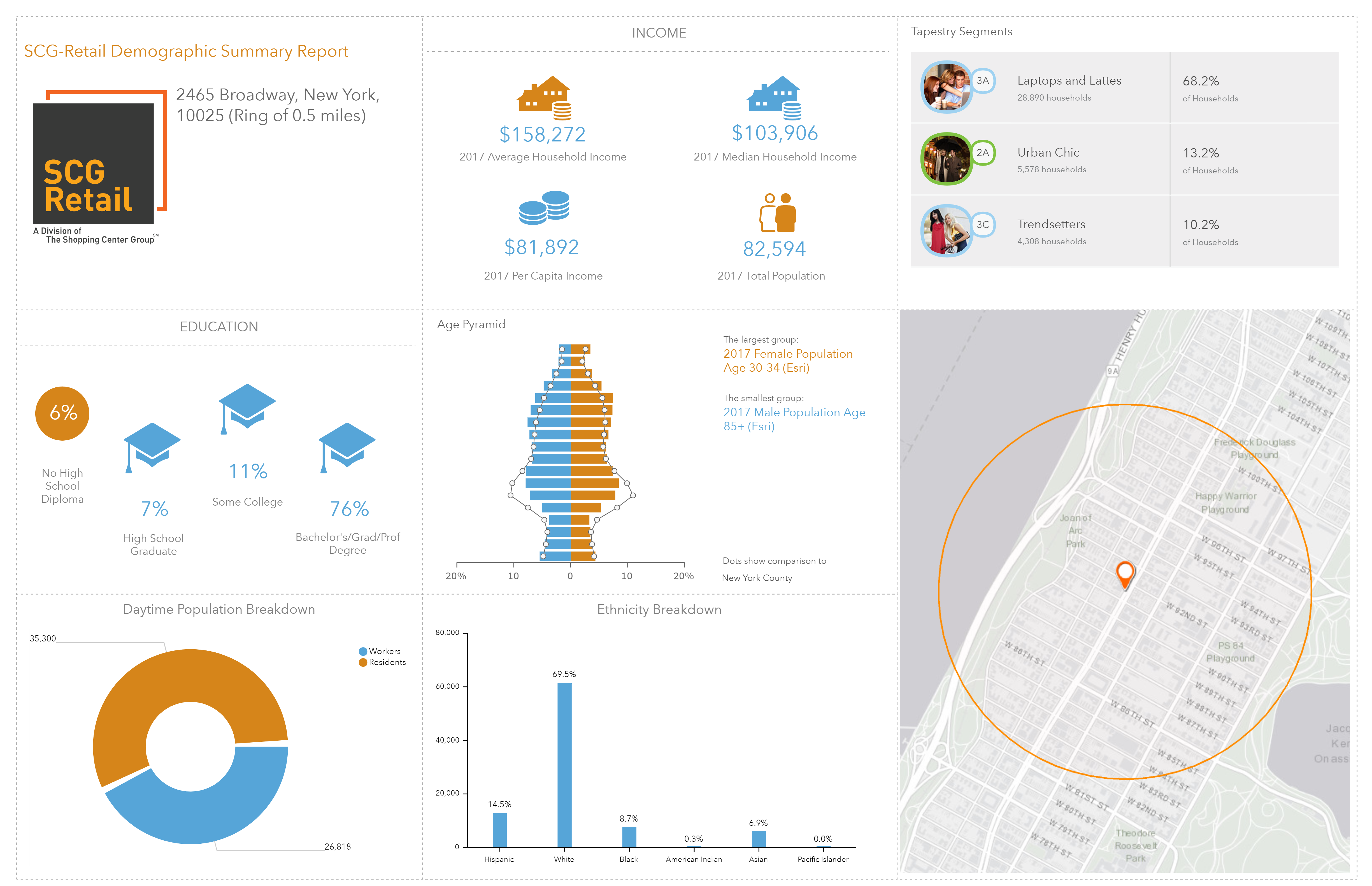
As part of this work, Geocove helped Livingston County centralize its licenses into one Esri organizational account, then set up and configured the County’s organization in the newly established Enterprise environment. Additionally, Geocove provided County planning staff with a technology transfer and introduction to ArcGIS Online / ArcGIS Portal maps and apps. As part of this work, Geocove’s staff rebuilt the County’s public and internal web applications in the newer and supported Esri architecture.
Through additional technical support and focused contracts, Geocove has designed and built solutions for Livingston County’s Department of Health (septic inspections and reports); Highway Department (sign inventory and editing tools, desktop editing, import and data cleanup and map updates); Sheriff’s Office / Office of Emergency Management (critical facilities and vulnerable population maps/apps and editing tools); and Economic Development (building inventory management system).
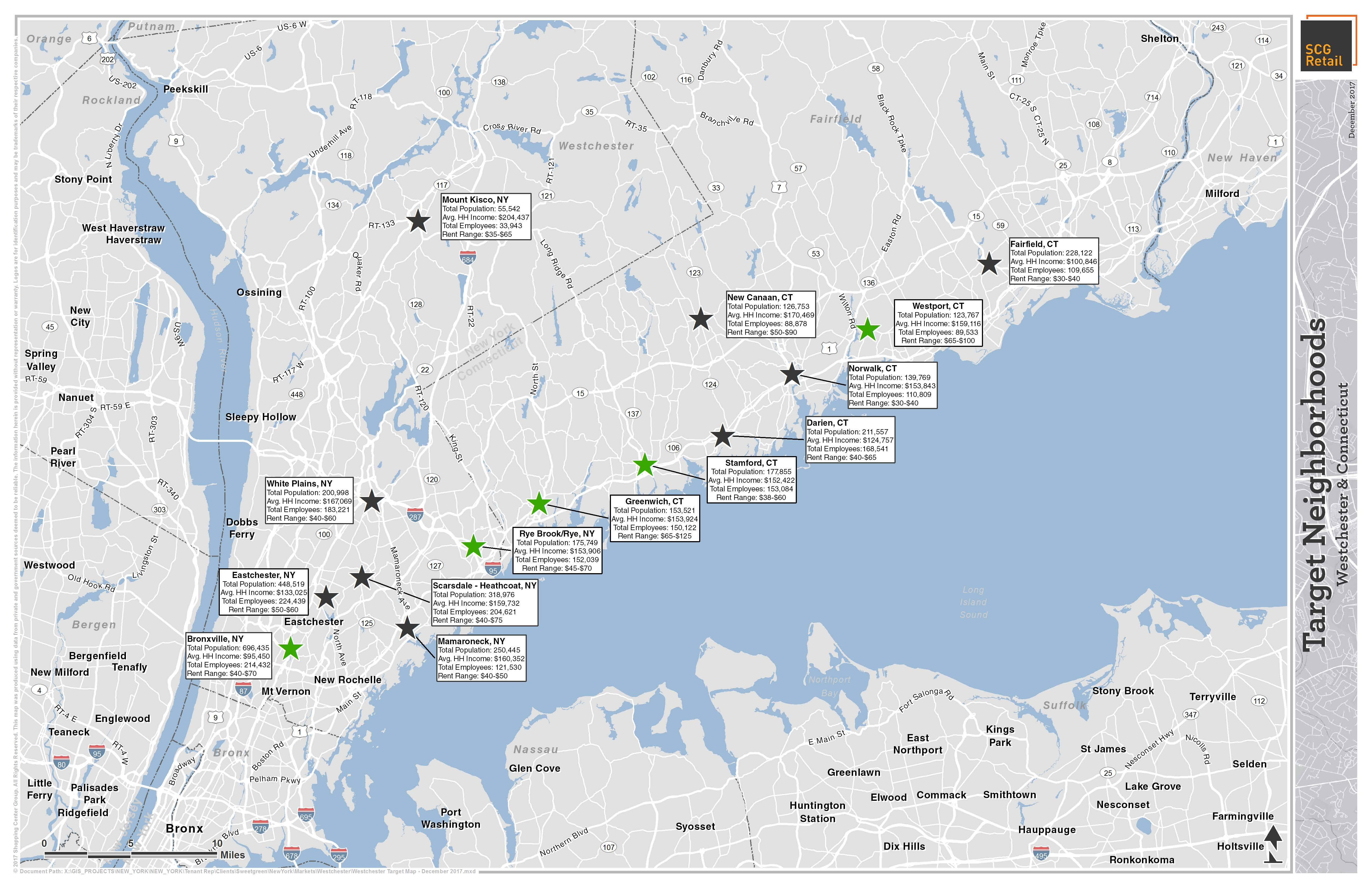
Other resulting applications include a road closure management app for emergency management, an election application to show election districts and polling locations, a facility locator application, and a story map for Economic Development’s Mural Walls program.
Contributions to the Profession
Geocove actively engages with the GIS community in Western NY, including offering free Lunch-and-Learns in their offices and organizing and participating in GIS Day events. Including the Esri Special Achievements in GIS award for Tonawanda, the company has also earned an Emerging Technology award from VEMA and the Public Information Award from the Florida Governor’s Hurricane Conference.
Contact:
Karyn Tareen GISP, President Direct 716.204.9431
Geocove Office 716.748.7585
247 Cayuga Rd., Suite 70
Cheektowaga, NY 14225
ktareen@geocove.com
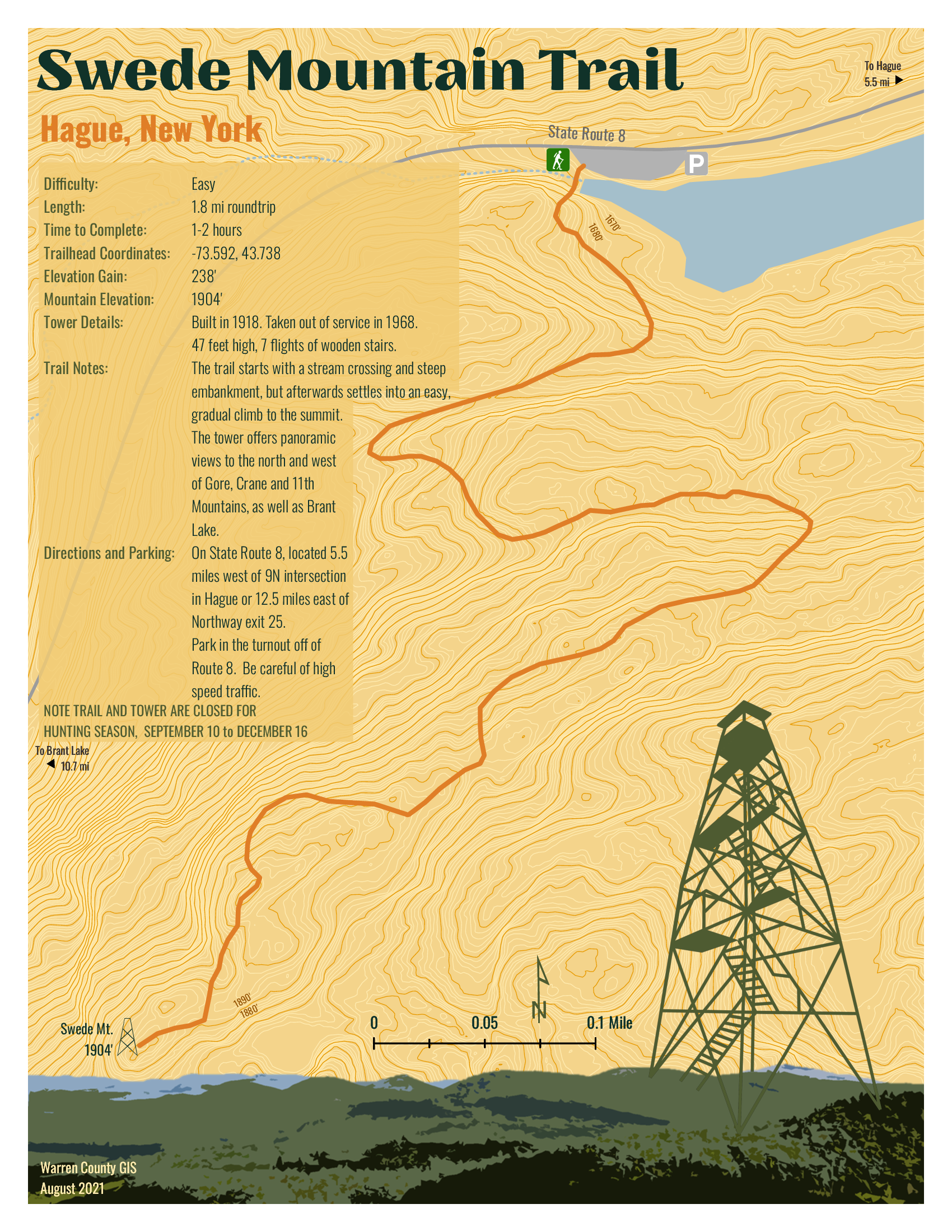
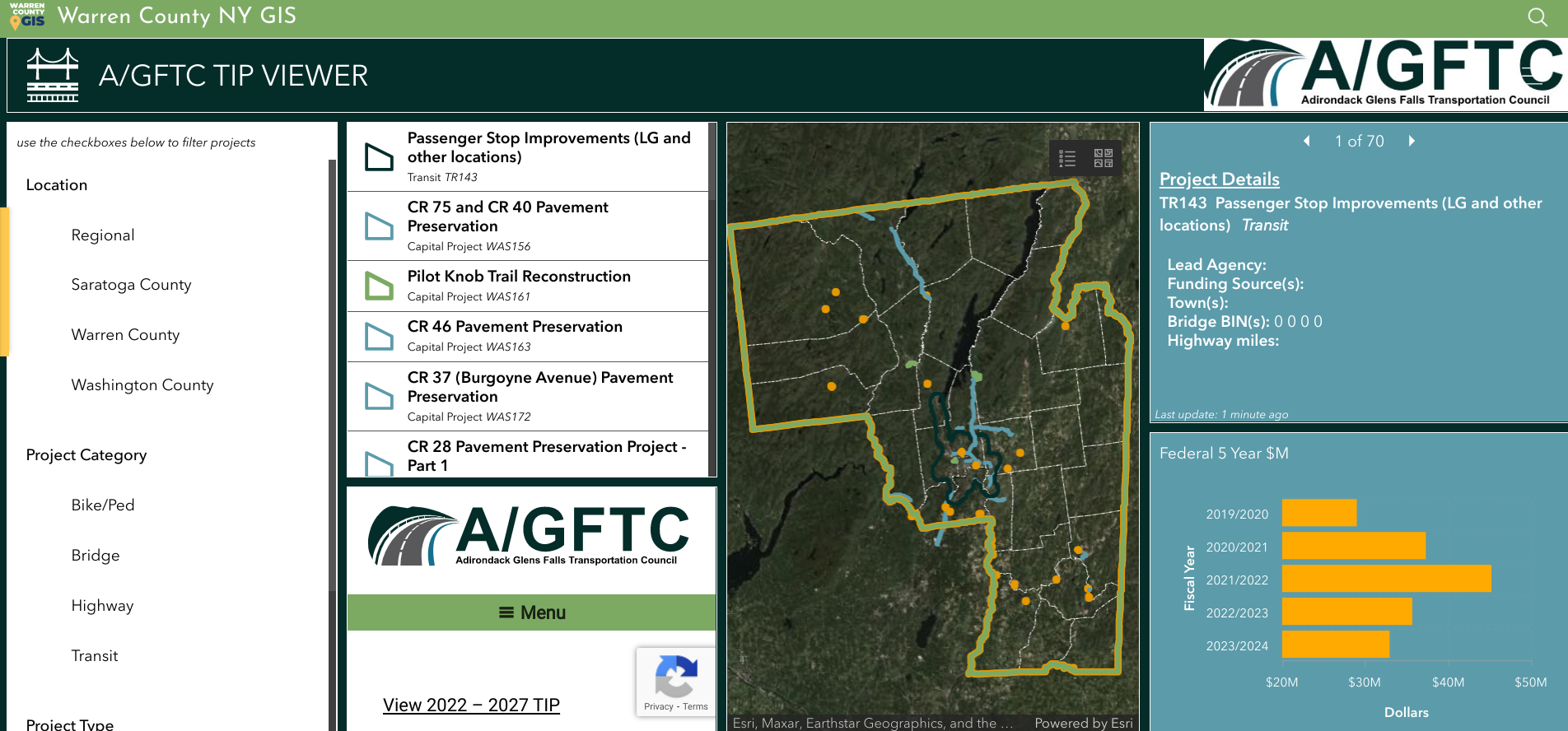
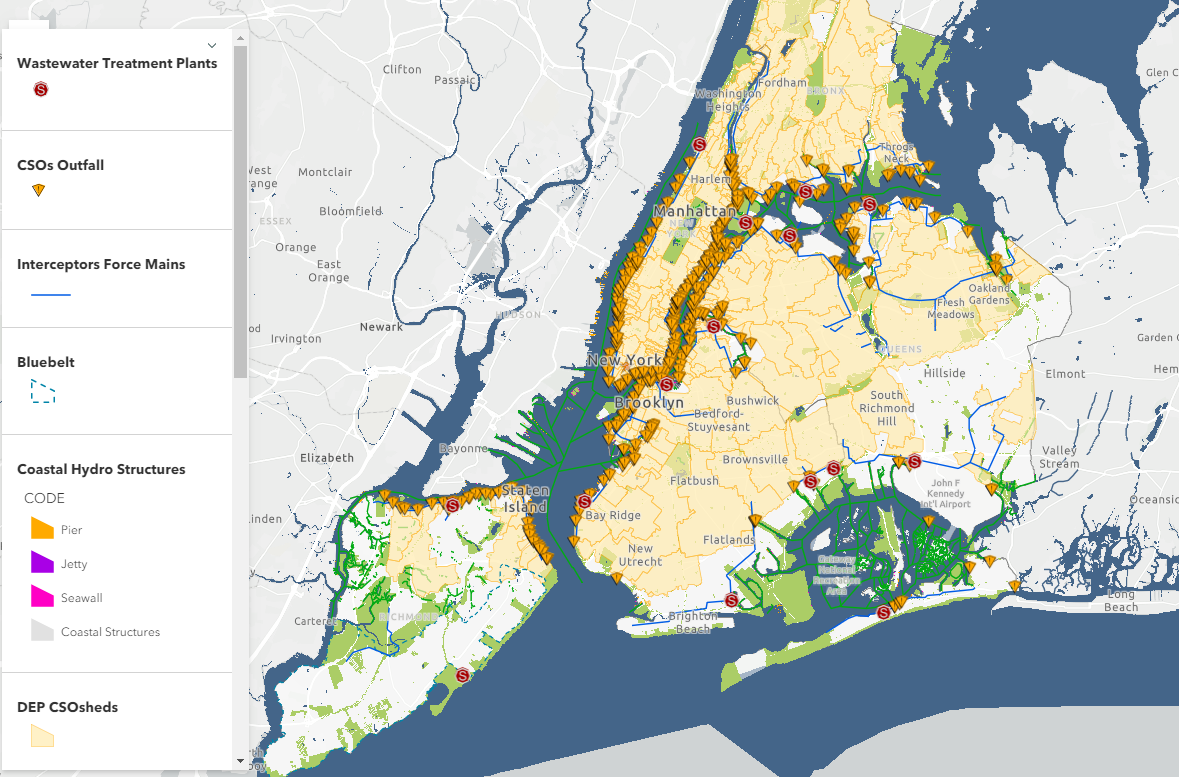
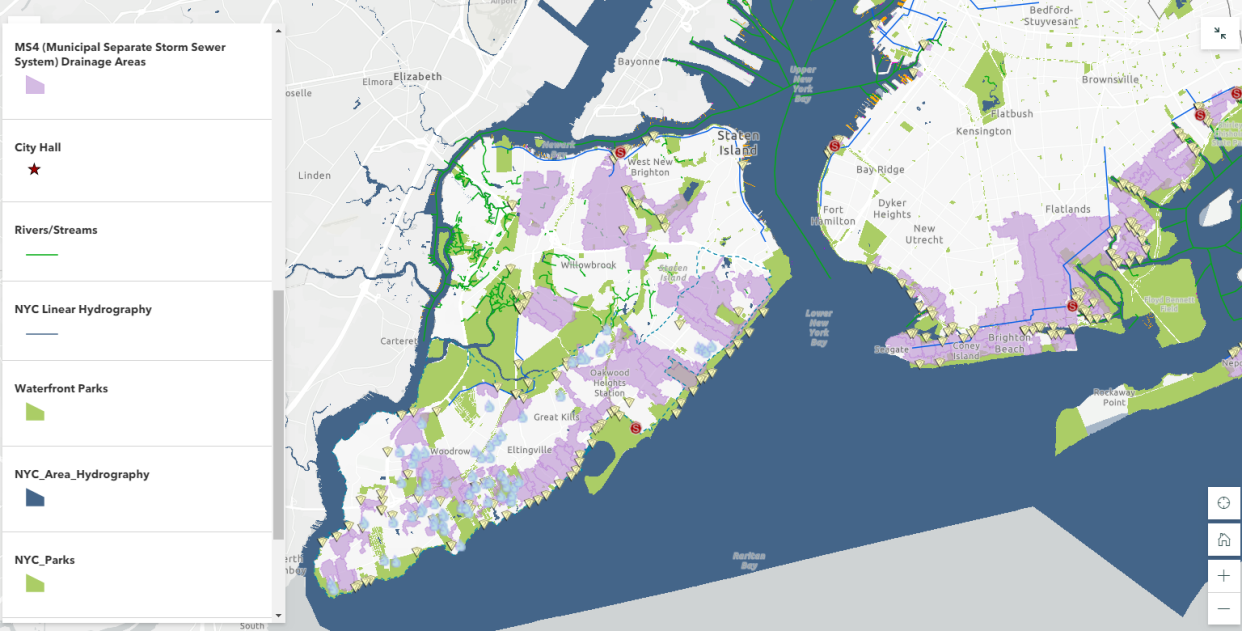
 While the
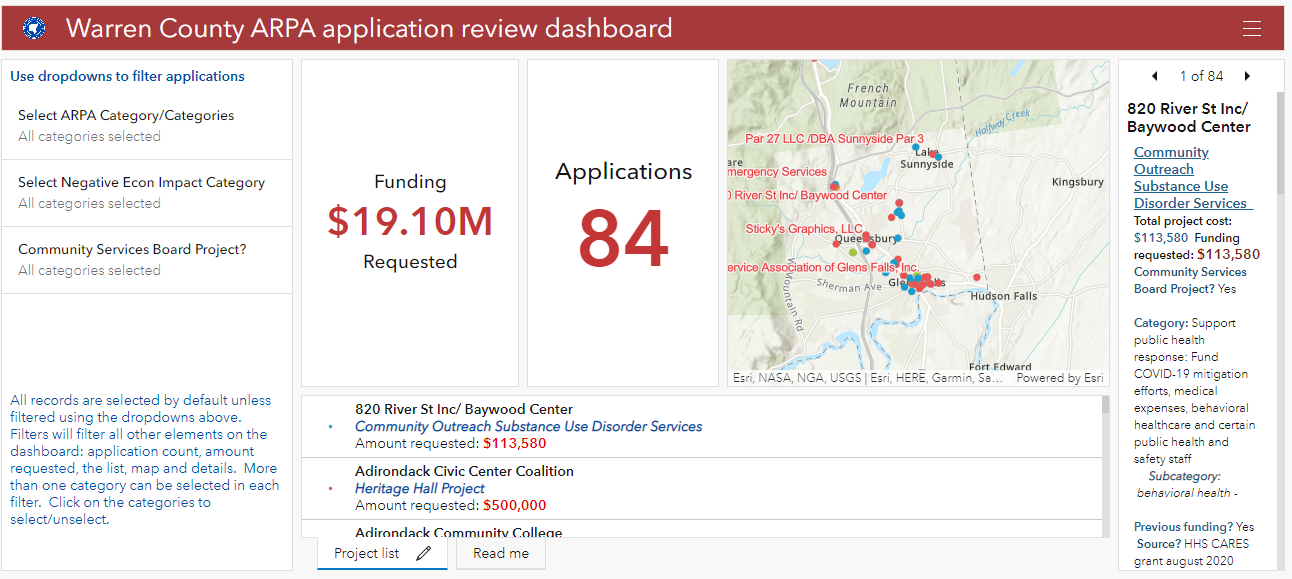
While the  One such MS4 DIY organization is Erie County which provides administrative and technical support to the
One such MS4 DIY organization is Erie County which provides administrative and technical support to the 

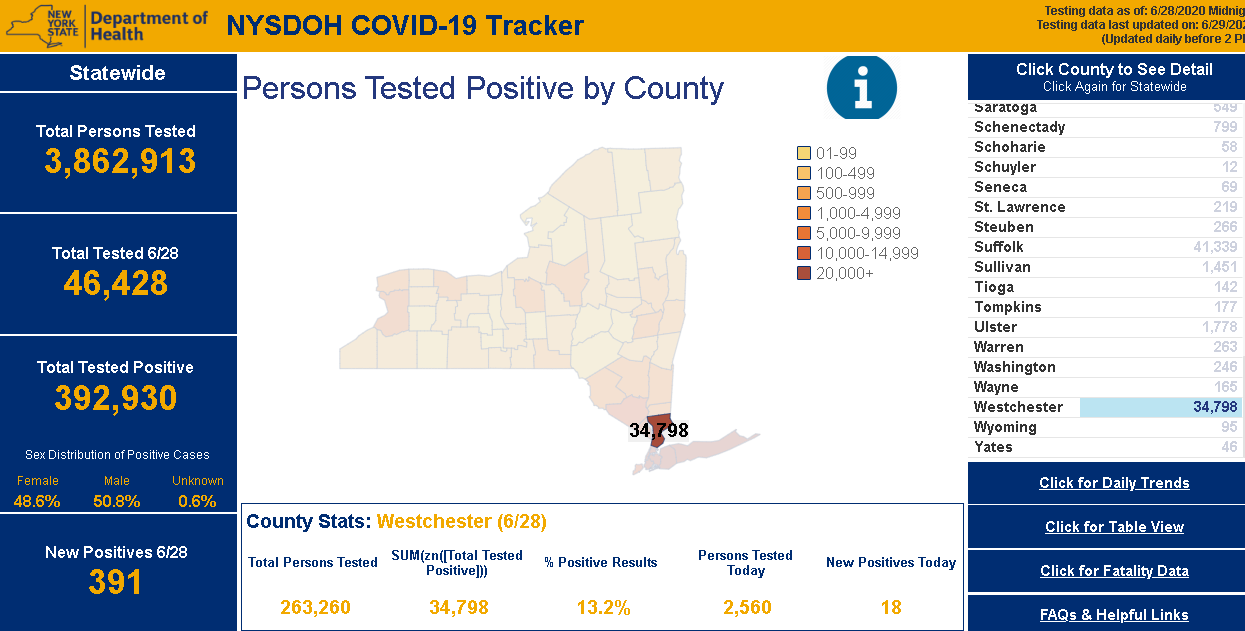
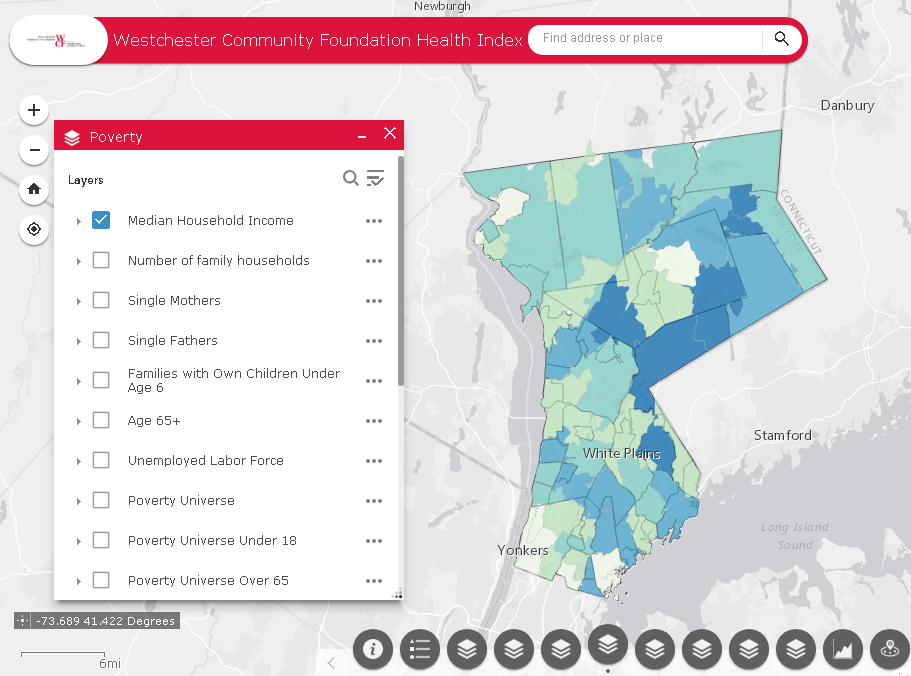
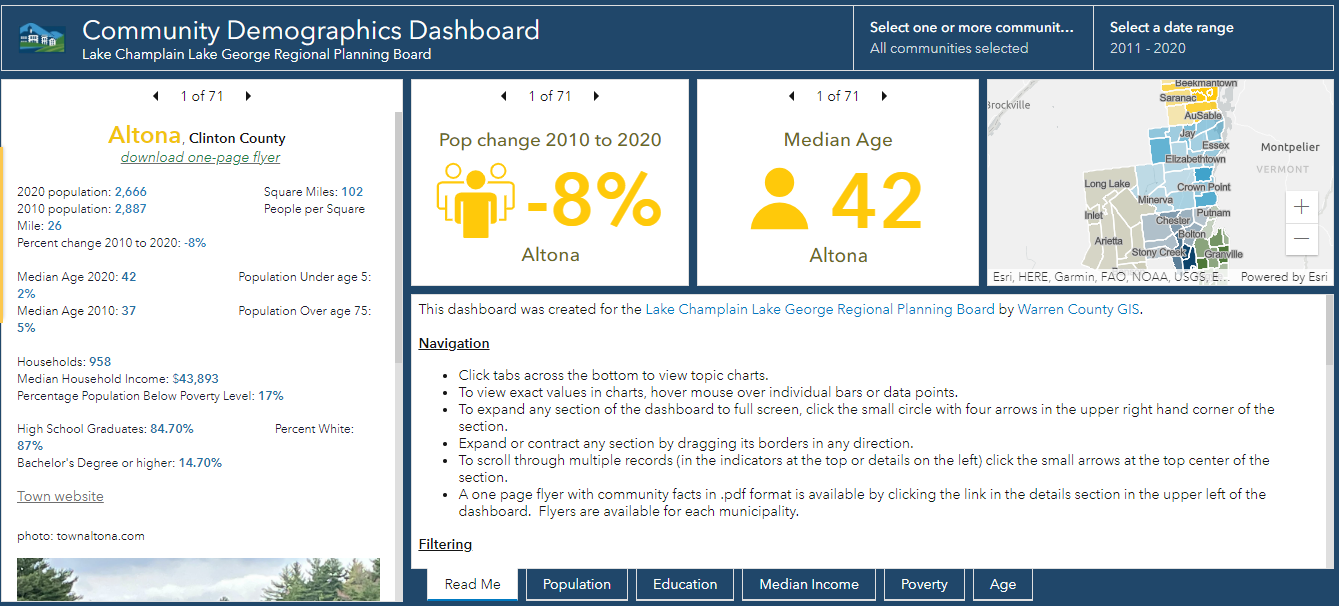
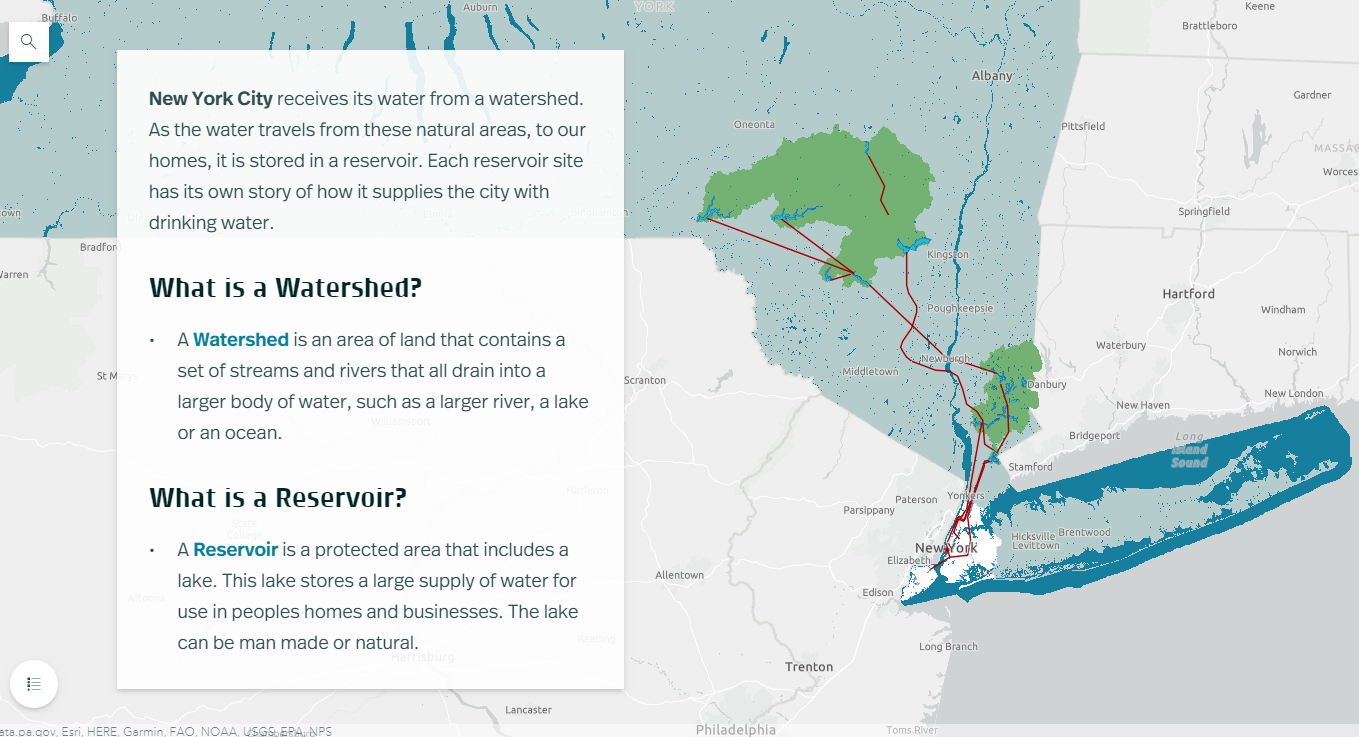
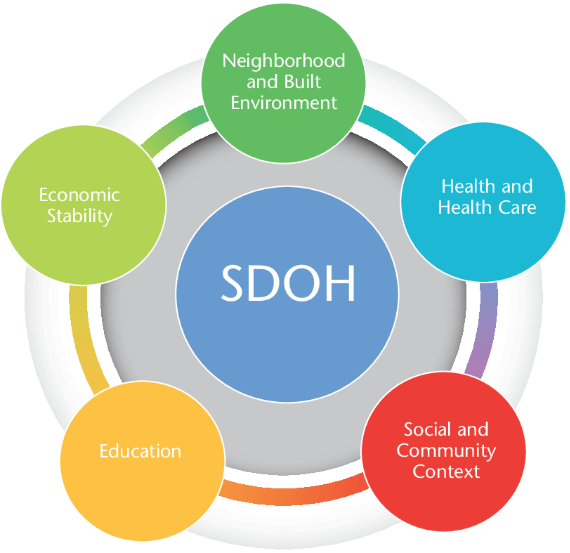 and tracking of social determinants of health. Universities, governmental and non-profit organizations now routinely collect such data and utilize GIS to help inform analysis and better decision-making, leading to stronger policies. The Healthy People 2020 Approach to Social Determinants of Health employs a
and tracking of social determinants of health. Universities, governmental and non-profit organizations now routinely collect such data and utilize GIS to help inform analysis and better decision-making, leading to stronger policies. The Healthy People 2020 Approach to Social Determinants of Health employs a