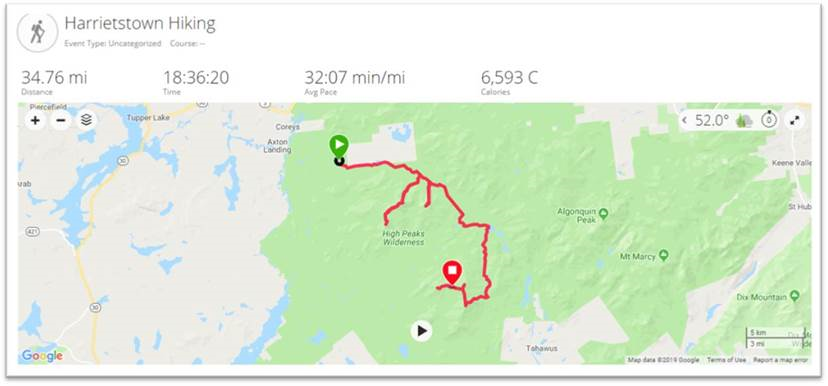
Daniel Munoz, GIS Manager, Orange County GIS Division, has been an integral part of the Orange County GIS program for over twenty years and involved in geospatial initiatives in municipalities across the county as well. Somewhat atypical of how other county programs across the Empire State originally evolved, Daniel led implementation of the countywide effort from its beginning from inside the Orange County Water Authority and later on overseeing development into key enterprise programs in the areas of Real Property Tax Services and Emergency Services. With Spanish being his native language, I also asked Daniel to offer any thoughts/ideas on how to expand and provide geospatial tools to the growing Spanish speaking populations across the Empire State. In further supporting this issue, this eSpatiallyNewYork post is published in both Spanish and English.
Daniel Muñoz, Gerente del SIG, Condado de Orange División de SIG, ha sido una parte integral del programa SIG del Condado de Orange por más de veinte años y también ha participado en iniciativas geoespaciales en los municipios del condado. Un poco diferente de cómo evolucionaron estos programas en otros condados en el Empire State, Daniel dirigió la implementación de los esfuerzos del condado desde el inicio en el Departamento de Agua del Condado de Orange y luego supervisó el desarrollo de programas claves en las áreas de Servicios de Impuestos de Bienes Inmuebles y Servicios de Emergencia. Como el español es su lengua materna, también le pedí a Daniel que ofreciera conceptos / ideas sobre cómo expandir y proporcionar herramientas geoespaciales a las crecientes poblaciones de habla hispana a través del Empire State. Para respaldar aún más esta situación, esta publicación de eSpatiallyNewYork es disponible tanto en español como en inglés.
1. eSpatiallyNewYork: Let’s start from the beginning. Where are you originally from and when/how did you end up in Orange County government?
Munoz: Here is the short story! I’m originally from Mexico City where I earned my Professional Engineer (P.E.) stripes. I graduated as an industrial engineer from the Autonomous Metropolitan University of Mexico City and initially worked as computer system analyst for an international kitchen appliance company. I was fine with reading English and working with computers programing languages, but struggled with conversational English. Since I had friends in the city, I decided to move to Boston, Massachusetts to learn English. While there I met a woman from Orange County which I married and ultimately moved to Orange County.
eSpatiallyNewYork: Empecemos por el principio. De donde eres originalmente y cuando o como terminaste en el gobierno del Condado de Orange?
Munoz: Esta es la historia corta! Soy originario de la Ciudad de México donde obtuve mi titulo de Ingeniero. Me gradué de Ingeniero Industrial de la Universidad Autónoma Metropolitana de la Ciudad de México inicialmente trabaje de Analista de Sistemas de Computación para una compañía internacional de electrodomésticos de cocina. No tenia problemas leyendo ingles y trabajando con lenguajes de programación de computadoras, pero me costaba trabajo el inglés conversacional. Decidí mudarme a Boston, Massachusetts para aprender inglés ya que tenia amigos en esa ciudad. Allí conocí a una mujer del Condado de Orange con la que me casé y finalmente me mudé al Condado de Orange.
2. eSpatiallyNewYork: What were your earliest Orange County GIS efforts?
Munoz: I started with the Orange County Water Authority (OCWA) which is a “cousin” of county government. My title then was digital systems analyst, which in hindsight, was “being in the right place at the right time”. When I moved here, Orange County had not developed an E-911 system, but OCWA had started gathering various databases and integrated computer mapping technology to create a county wide Geographic Information System. Which ultimately led to OCWA starting to serve a significant supporting role in developing the new computerized E-911 system. It was during this time I developed my own passion for GIS technology. Since then I have learned about and worked in the fields of emergency management, planning, tax mapping, public works, and many other areas of county government. We are providing and integrating data for all services!
eSpatiallyNewYork: ¿Cuáles fueron tus primeros esfuerzos de SIG en el Condado de Orange?
Munoz: Comencé trabajando para Orange County Water Authority (OCWA) la cual es un agencia del gobierno del Condado de Orange. Mi título entonces era analista de sistemas digitales, en retrospectiva, fue “estar en el lugar correcto en el momento adecuado”. Cuando me mude aquí, El Condado de Orange no había desarrollado el Sistema E-911, OCWA había comenzado a recopilar varias bases de datos y tecnología integrada de mapeo por computadora para crear un Sistema de Información Geográfica para todo el condado. Lo que finalmente llevó a que OCWA comenzara a desempeñar un importante papel de apoyo en el desarrollo del nuevo sistema computarizado E-911. Fue durante este tiempo que desarrollé mi propia pasión por la tecnología SIG. Desde entonces, he aprendido y trabajado en los campos de gestión de emergencias, planificación, asignación de impuestos, obras públicas y muchas otras áreas del gobierno del condado. ¡Estamos proporcionando e integrando datos para todos tipo de servicios!
3. eSpatiallyNewYork: Do you remember the version of ARC/INFO you got started with and what ESRI products are you using today?
Munoz: Oh boy. I do and this really dates me! My GIS experience didn’t start with ARC/INFO, I started with ArcView 1.0 with option to update to 1.0a. I still have the box almost intact with the 5¼” installation floppy disks (picture below). We did most of the work with ArcCAD an ESRI plugin for AutoCAD. My first interaction with ARC/INFO was at Version 7. Nowadays we try to keep up to date as much as possible but avoiding the “bleeding edge”. We are in the process of moving our full enterprise GIS to V 10.6.1. I use the full ArcGIS suite including ArcServer and ArcMap with the following extensions: Network Analyst, Spatial Analyst and 3D Analyst. I have tried ArcGIS Pro but still has some issues. As far as the web environment, I created all of our websites with the old ESRI flash builder and have started to update them with Web AppBuilder.

Like many others across the state, Daniel got his start with desktop ArcView software. Still an ESRI favorite to seasoned GIS professionals.
eSpatiallyNewYork: ¿Recuerdas la versión de ARC/INFO con la cual comenzaste y que productos de ESRI usasactualmente?
Munoz: Ay Caramba! Recuerdo bien y revela cuanto tiempo ha pasado! Mi experiencia en SIG no comenzó con ARC/INFO, comencé con ArcView 1.0 con la opción de actualizar a 1.0a. Todavía tengo la caja casi intacta con los discos de instalación de 5¼ ” (imagen abajo). La mayor parte del trabajo fue echo con ArcCAD una extensión de ESRI para AutoCAD. Mi introducción con ARC/INFO fue en la versión 7.0. Hoy en día tratamos de mantenernos actualizados tanto como sea posible, pero evitamos estar a la “vanguardia”. Estamos en el proceso de actualizar nuestro completo SIG a la versión 10.6.1. Uso el paquete completo de ArcGIS, incluyendo ArcServer y ArcMap con las siguientes extensiones: Network Analyst, Spatial Analyst y 3D Analyst. He tratado ArcGIS Pro pero todavía tiene algunos problemas. Entorno de la web, construí todas nuestras paginas de web con la antigua tecnología de flash pero ya comencé a actualizarlos con la tecnología de Web AppBuilder.
4. eSpatiallyNewYork: You left GIS for a while to take another position in County Information Technology – but then came back to GIS. Tell us about that.
Munoz: For me, GIS & IT always go hand to hand. While working for the County, I always found myself splitting my work projects between GIS & IT. At the beginning of my career in order to build a better GIS program I had to build a better IT infrastructure. During this time, I obtained a Windows & Network professional certification. Having this expanded IT background gave me the opportunity to move to an IT Director position which at the time was a good professional advancement for me. Two years ago, the County decided to upgrade the County’s GIS and I was asked to be part of the team to interview candidates and proposals. Going through this process reminded me how much I enjoyed geospatial technology so I made the decision to move back to managing the Orange County GIS program.
eSpatiallyNewYork: Dejaste el SIG por un tiempo para tomar otra posición en el departamento de Información Tecnología del Condado – pero luego regresaste al SIG. Platícanos a cerca de esto.
Munoz: Para mí, el SIG & la IT siempre van de la mano. Mientras trabajaba para el Condado, siempre me encontraba dividiendo mi tiempo y proyectos de trabajo entre SIG y IT. Al comienzo de mi carrera, para construir un mejor sistema de SIG tuve que construir una mejor infraestructura de IT. Durante este tiempo, obtuve una certificación profesional de Windows y Redes. Teniendo esta experiencia ampliada en IT me dio la oportunidad de cambiarme a un puesto de director de IT, lo que en ese momento fue un buen avance profesional para mí. Hace dos años, el Condado decidió actualizar el SIG del Condado y me pidieron que formara parte del equipo para entrevistar a los candidatos y sus propuestas. Ser parte de este proceso me recordó lo mucho que disfrutaba la tecnología geoespacial, así que tomé la decisión de regresar a dirigir el SIG del Condado de Orange.
5. eSpatiallyNewYork: So which areas of County government are the biggest users of geospatial technology?
Munoz: Definitely Emergency Services! They have three divisions working 24×7 using and creating data everyday. Second would be the Planning Department and following very close the Department of Public Works.
eSpatiallyNewYork: Entonces, ¿Qué áreas del gobierno del Condado tiene los mayores usuarios de tecnología geoespacial?
Munoz: Definitivamente el departamento de Servicios de Emergencia! Este departamento tiene tres divisiones que trabajan 24×7 usando y creando datos todos los días. Segundo sería el Departamento de Planificación y siguiéndolo muy de cerca el Departamento de Obras Públicas.
6. eSpatiallyNewYork: The County still offers hardcopy maps, shapefiles, and other products for download. How has this changed, if at all, over the years?
Munoz: It seems that technology is always driving the associated GIS changes. The GIS offices are quieter these days as the phones don’t ring as much. We use to answer the phone constantly to take requests, return calls to inform the caller their request had been completed. Today, our online automated GIS request website has taken care of many of these issues. Individuals can create accounts, make mapping or data requests, and be notified when the request has been fulfilled with instructions on how to obtain the request. The website also has an area for data downloads and can notify registered users when County data layers have been updated by our staff.
eSpatiallyNewYork: El Condado todavía ofrece mapas impresos, shapefiles y otros productos para descargar. ¿Cómo ha cambiado esto, si es que ha cambiado, con los años?
Munoz: Parece que la tecnología siempre está impulsando los cambios asociados al SIG. Las oficinas de SIG son más silenciosas en estos días ya que los teléfonos no suenan tanto. Solíamos contestar el teléfono constantemente para recibir pedidos, devolver llamadas a nuestros usuarios para informarles que su pedido esta completo. Hoy en día, nuestro sitio de web tiene un sistema de pedidos automatizados y se ocupa de muchos de estos problemas. Las personas pueden crear cuentas, realizar pedidos de mapas o datos y recibir notificaciones automatizadas cuando el pedido se haya cumplido e instrucciones sobre cómo obtenerlo. El sitio web también tiene un área para descarga de datos y puede notificar a los usuarios registrados cuando nosotros actualizamos las bases de datos del Condado.
7. eSpatiallyNewYork: Any integration with the AutoCAD environment?
Munoz: Currently, a small group of engineers from DPW and the tax mapping division are the only ones that still use AutoCAD. Some years ago the tax mappers started to maintained the parcel boundaries from their tax maps in an enterprise database with AutoCAD. As previously mentioned, our current GIS upgrade project includes moving the full tax map maintenance program to our ArcGIS environment. Stay tuned!
eSpatiallyNewYork: ¿Alguna integración con el programa de AutoCAD?
Munoz: Actualmente, solo un pequeño grupo de ingenieros de el Departamento de Obras Públicas y la división de mapas de cadastro son los únicos que todavía utilizan AutoCAD. Hace algunos años, los mapas de cadastro se comenzaron a mantener a través de una base de datos con AutoCAD. Como se mencionó anteriormente, nuestro proyecto actual de actualización del SIG incluye mover el programa de mantenimiento de mapas de cadastro a nuestro sistema de ArcGIS. ¡Mantente al tanto!
8. eSpatiallyNewYork: As GIS Manager, what are your biggest challenges today?
Munoz: I would have to say staffing. Believe it or not in the last two years I have had to replace the GIS technician positions four times. While each time each person has been a competent young professional, It seems to me the new generation of GIS technicians wants to keep moving on with the next opportunity for advancement. As opposed to staying in one place for while and building a career in one place. I find myself training people to see them gone within 6 – 12 months. A huge challenge!
eSpatiallyNewYork: Como Gerente de SIG, ¿cuáles son tus mayores desafíos hoy?
Munoz: Tendría que decir que es el personal. Lo creas o no, en los últimos dos años he tenido que reemplazar las posición de técnico en SIG cuatro veces. Cada vez la persona ha sido un joven profesional competente, pero me parece que la nueva generación de técnicos en SIG siempre anda buscando la próxima oportunidad de avance. A diferencia de permanecer en un lugar por un tiempo y construir una carrera en ese lugar. Me encuentro entrenando personas para que desaparezcan en los próximos 6 – 12 meses. ¡Un gran reto!
9. eSpatiallyNewYork: What’s the next big geospatial thing in Orange County?
Munoz: The County is finalizing the Orange County Shared Services Property Tax Savings Plan. One section in particular reads:
The County of Orange will offer geographic information services (GIS) to any and all of its 43 municipalities. This will include all cartography and geographic data services such as map development, maintenance and printing.
Coordinating and standardizing 43 municipalities will be our biggest project and will keeps us busy for a good while. I’m hoping for staff continuity!
eSpatiallyNewYork: ¿Cuál es la próxima gran cosa geoespacial en el Condado de Orange?
Munoz: El Condado está finalizando el Plan de Servicios Compartidos de Ahorro de Impuestos de la Propiedad del Condado de Orange. Una sección en particular dice:
El Condado de Orange ofrecerá servicios de información geográfica (SIG) a todos y cada uno de sus 43 municipios. Esto incluirá todos los servicios de cartografía y servicio de datos geográficos, como el desarrollo de mapas, el mantenimiento y la impresión.
Coordinar y estandarizar 43 municipios será nuestro mayor proyecto y nos mantendrá ocupados por un buen rato. ¡Espero y el personal sea continuo entonces!
10. eSpatiallyNewYork: You are of Hispanic background. Do you have any thoughts or ideas on how GIS technology could be extended to the regional Spanish speaking population? Where and how would you start?
Munoz: The beauty of GIS is that it can help everyone in so many ways. But the challenge continues to be building applications which are relevant, accessible, and easy to use. Research show that Hispanics are less likely to have an internet connection at home. Hispanics are early technology adopters, and Hispanics are mobile-first community. These statements contradict each other a bit but it is because the Hispanic demographic is young. Based on this information I would focus available resources to build, design and post GIS apps in Spanish on mobile platforms (cell phones and tablets) where we know Hispanics are spending their time. These early adopters will spread the message among their social groups faster than any other method.
eSpatiallyNewYork: Eres de origen hispano. ¿Qué piensas o que ideas tienes sobre cómo la tecnología de Sistemas de Información Geográfica (SIG) podría extenderse a la población regional de habla hispana? ¿Dónde y cómo empezarías?
Munoz: Lo bonito del SIG es que ayuda a todos, pero debemos asegurarnos de distribuirlo a ellos. Las investigaciones demuestran que los Hispanos tienen la menor probabilidad de tener una conexión de internet en casa, los Hispanos adoptan la tecnología tempranamente y son una comunidad que usan los dispositivos móviles primero. Estas declaraciones se contradicen un poco, pero es debido a que la demografía hispana es joven. Basado en esta información yo pondría todos los recursos disponibles en crear, diseñar y publicar aplicaciones de SIG en plataformas móviles (teléfonos celulares y tabletas) donde sabemos que los Hispanos pasan la mayoría de su tiempo. Estos pioneros difundirán el mensaje atreves de sus redes sociales más rápido que cualquier otro método.
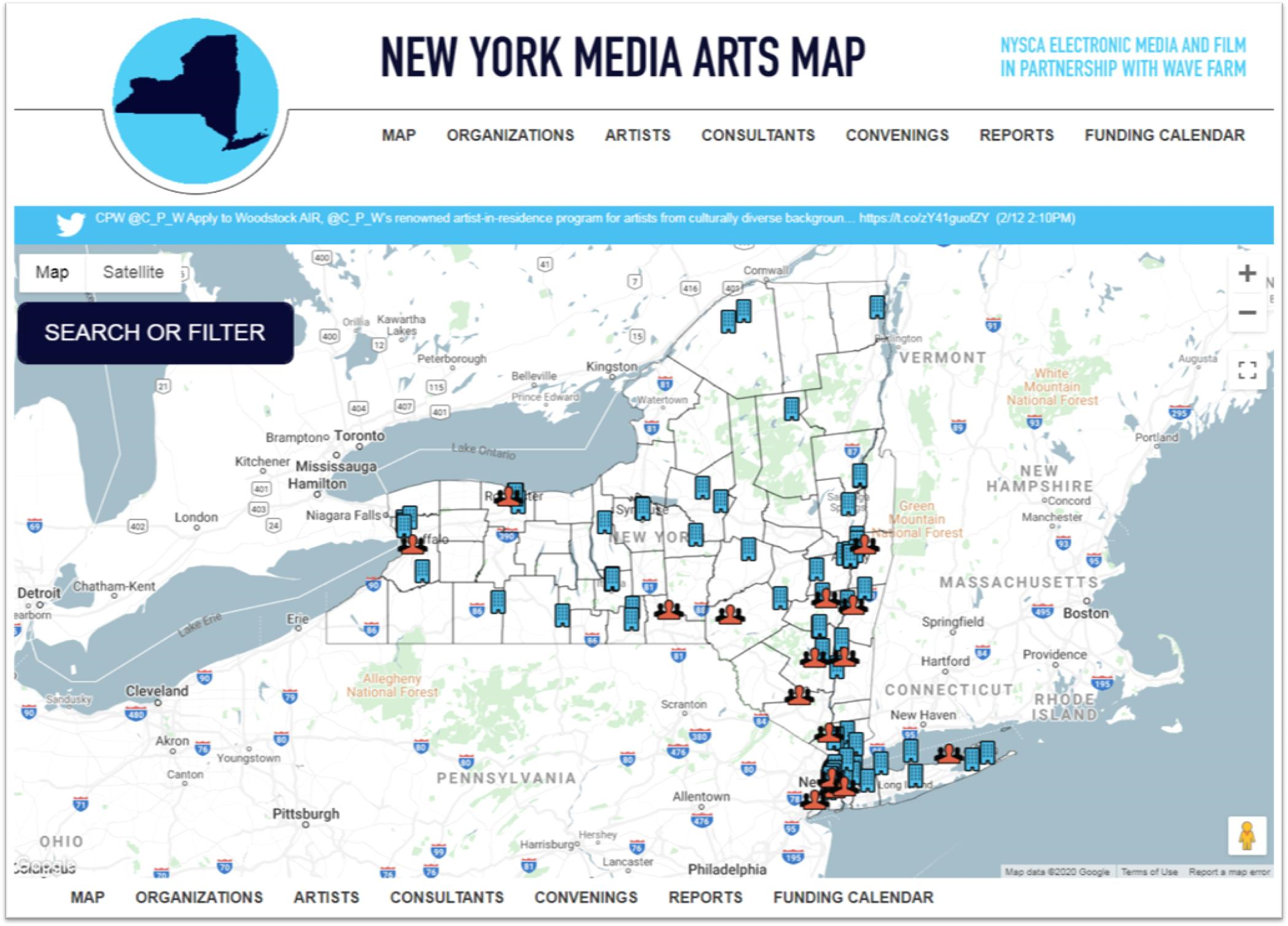
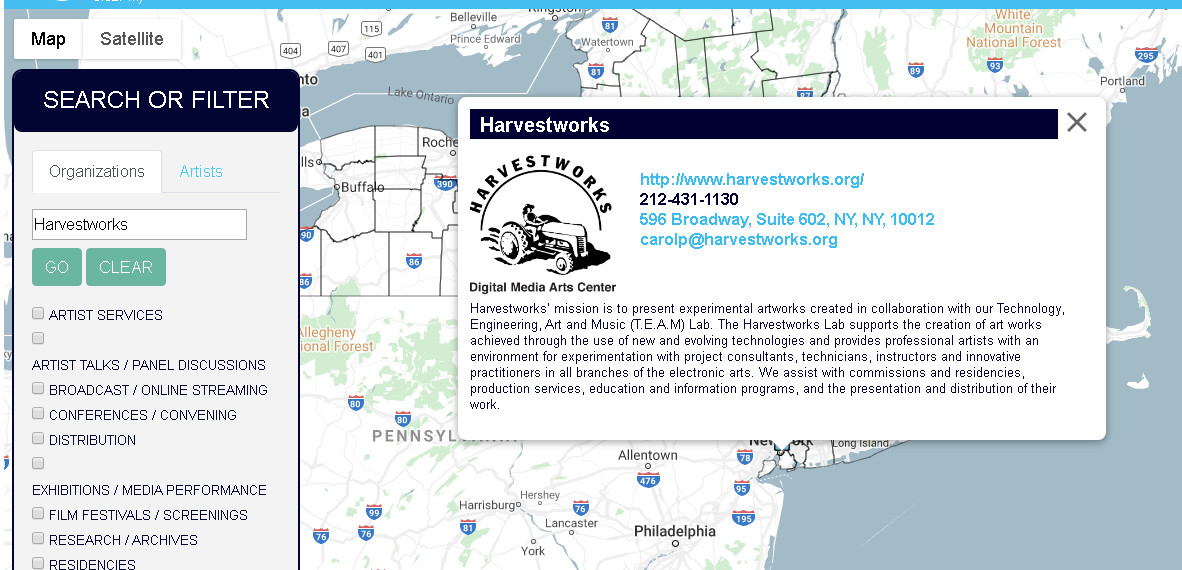
 The report was published by the Harvestworks Digital Media Arts Center and The New York City Urban Field Station which is a partnership of the U.S. Forest Service, New York City Department of Parks and Recreation, and the Natural Areas Conservancy. (The Field Station in NYC supports the Arts and Humanities Residency Program. Check out the Summer 2018 Moon Arrow project – a time lapse compilation of the Moon Arrow pointing to the moon on New York City shorelines). Open data, building code and hackathons in the geospatial space of your interest? Then take a look the work of the School for Poetic Computation. And how about drones? While the technology is evolving incredibly fast, there was the 2018 Art Omi, Wave Farm and eteam live performance of The Aerial Actor which focused on the rising use of drones in science and art. Actual drones were used as both carriers of messages and actors in the performance. “The Map is a vital resource identifying art and technology projects and activity throughout New York State supported by NYSCA Electronic Media & Film”, says Galen Joseph-Hunter, Executive Director, Wave Farm. “It is also a useful tool for showing a geographic picture of how support is distributed throughout the state.”
The report was published by the Harvestworks Digital Media Arts Center and The New York City Urban Field Station which is a partnership of the U.S. Forest Service, New York City Department of Parks and Recreation, and the Natural Areas Conservancy. (The Field Station in NYC supports the Arts and Humanities Residency Program. Check out the Summer 2018 Moon Arrow project – a time lapse compilation of the Moon Arrow pointing to the moon on New York City shorelines). Open data, building code and hackathons in the geospatial space of your interest? Then take a look the work of the School for Poetic Computation. And how about drones? While the technology is evolving incredibly fast, there was the 2018 Art Omi, Wave Farm and eteam live performance of The Aerial Actor which focused on the rising use of drones in science and art. Actual drones were used as both carriers of messages and actors in the performance. “The Map is a vital resource identifying art and technology projects and activity throughout New York State supported by NYSCA Electronic Media & Film”, says Galen Joseph-Hunter, Executive Director, Wave Farm. “It is also a useful tool for showing a geographic picture of how support is distributed throughout the state.”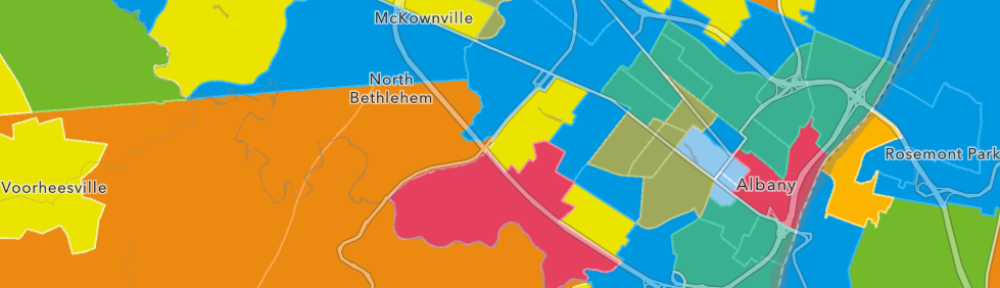
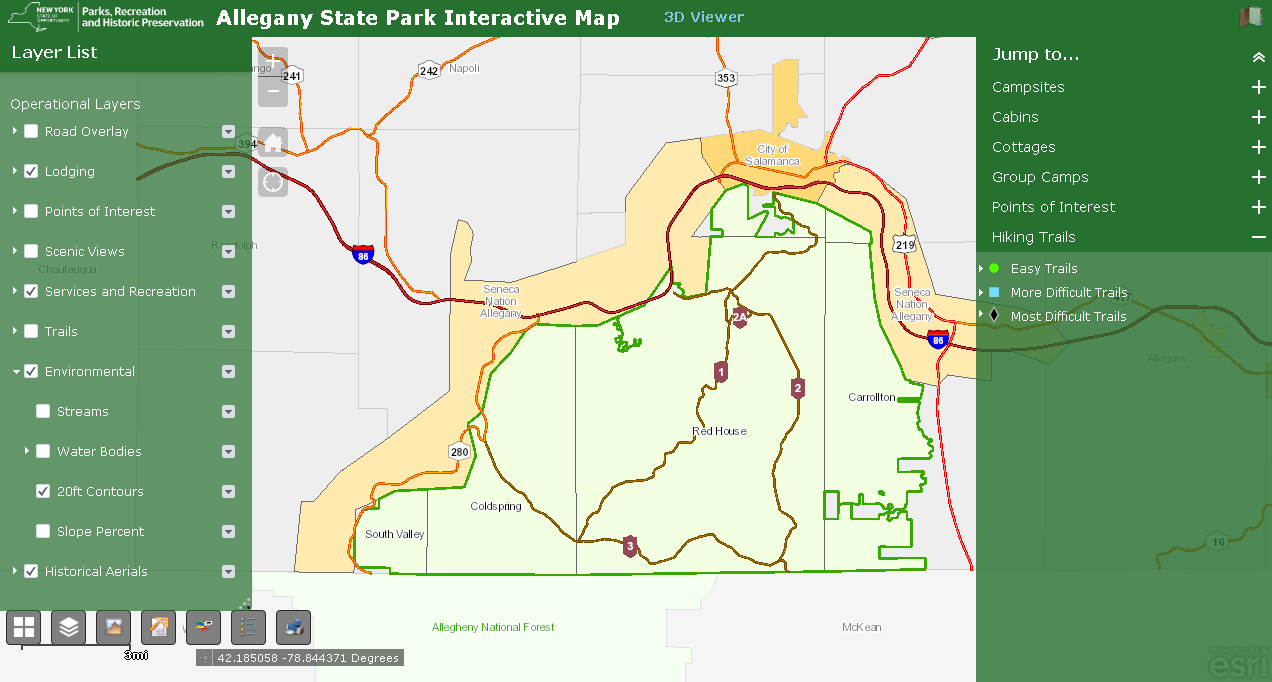
 Founded by Javier de la Torre, CARTO is a diverse and expanding company which includes data scientists, geospatial analysts, cartographers, software developers and engineers, visualization experts, and web designers focusing on Location Intelligence. Most recently in May 2019, CARTO expanded its worldwide professional service portfolio offerings by
Founded by Javier de la Torre, CARTO is a diverse and expanding company which includes data scientists, geospatial analysts, cartographers, software developers and engineers, visualization experts, and web designers focusing on Location Intelligence. Most recently in May 2019, CARTO expanded its worldwide professional service portfolio offerings by 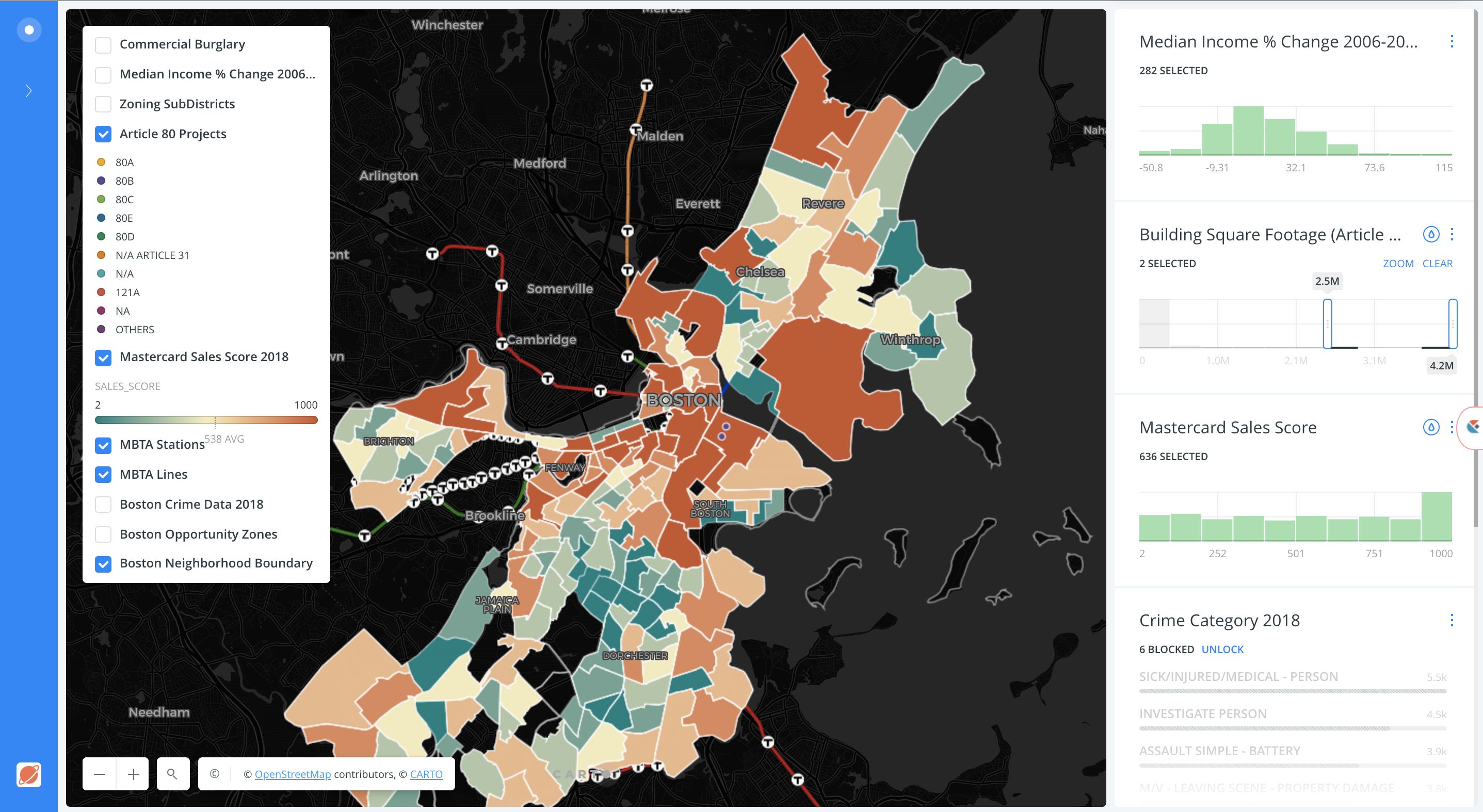
 I had the opportunity to attend the
I had the opportunity to attend the